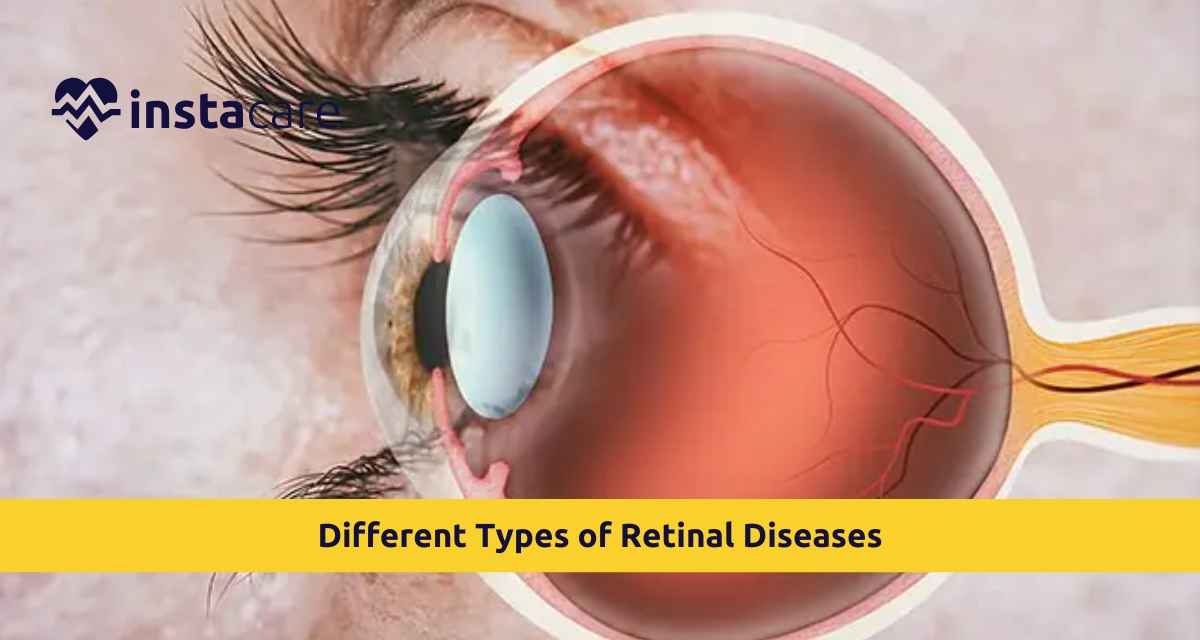
The retina is said to convert light into a neural signal in order to depict an image with the help of visual signals within the brain. Left untreated, retinal disease may lead to even greater vision loss to complete loss of vision or even total blindness. Proper diagnosis and handling can be realized with knowledge on different types of retinal disease. This is the article that will outline the forms of retinal disease, etiology, its manifestations, as well as treatment approaches.
Understanding the Retina
What is the Retina?
Retina is the tissue that is usually thin in texture and
placed in a rear side part of the eyes. The structures include rods, cones,
light cells, and dark cells responsible for detecting light. It plays the role
of aiding humans to see visually, and injury or disease damage can have
negative effects on seeing things clearly.
The preservation of vision requires an early detection of
retinal diseases. Regular eye examinations, especially for those having risk
factors, identify the problems before more severe stages develop.
Types of Retinal Diseases
1. Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a micro vascular disorder of the
retina that occurred due to diabetes. High blood sugar also affects the blood
vessels they can be damaged they become leaky or swollen or they develop where
they should not.
- Blurred or blurring of vision
- Dark spots or floaters in the field of view
- Poor night vision
- Vision loss
Treatment Plans:
- Photocoagulation may seal the leaking blood vessels by laser
treatment
- Medications: Anti-VEGF; injections that prevent abnormal
blood vessel growth and reduce swelling
- Surgery: Vasectomy in some instances, in order to remove
blood from the vitreous cavity
2. Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
Overview: AMD is one of the macular disorders wherein
central vision lost gradually. One of the predominant causes of aging-related
blindness.
Types
- Dry AMD: It possesses macula atrophy and drusen-the yellow
deposits within this. Dry AMD advances very slowly, and over time, will cause
vision loss.
- Wet AMD: The condition is characterized by the formation of
new blood vessels beneath the retina that leak and result in a loss of vision.
Symptoms and Signs:
- Distorted or wavy vision
- Blurred faces
- Dark holes or empty spaces within central vision
Treatment Options
- Nutritional Supplements: Some vitamins and minerals are
known to delay the progression of dry AMD.
- Anti-VEGF Injections: The medications are delivered by an
eye injection in order to block wet AMD at its sites, reducing formation of new
or faulty vessels.
- Photodynamic Therapy: It involves giving the light-sensing
medication on areas selectively targeting abnormal blood vessels in a targeted
procedure for killing defective vessels.
3. Retinal Detachment
It is characterized as separation of retina from the choroid. A severe consequence if untreated immediately would include loss of sight forever.
Causes
- Ocular trauma
- Ocular conditions
- Severe myopia or near-sightedness
- Symptoms
- Sudden floater or flashing lights in the eyes
- A shadow or curtain obscuring a part of the visual field
- Sudden vision loss
Treatment Options:
- Laser Surgery: These surgeries are used to repair minor
tears or holes in the retina.
- Pneumatic Retinopexy: A gas bubble is inserted into the eye
to make the retina mend against the wall.
- Scleral Buckling: The silicone band is placed around the eye to keep the retina in place.
View More: Can You Use Salicylic Acid With Retinol
4. Retinitis Pigmentosa
Overview: RS is rather more of a generic term applied to
hereditary retinal diseases that cause impaired photoreceptor layer. This may
cause pallor, night blindness and slow progressing contraction of outer visual
fields or visual field.
Symptoms:
- Poor vision in dim light (night blindness)
- Progressive loss of peripheral vision (tunnel vision)
- Blurred vision
Treatment:
- Genetic Counseling: Inherited nature of the disease
- Vitamin A Supplements: Some studies suggest that high doses
may retard the progression of the disease.
- Low Vision Aids: Devices to assist with vision loss.
5. Central Serous Chorioretinopathy (CSR)
Summary: CSR is believed to be diagnosed with the fluid
accumulation beneath the retina leading to blurring. It is commonly reported in
young-to-middle-aged males, and often it is reported during stress.
Symptoms:
- The center vision is not clear or has been altered
- Shadows will appear on the center vision
- Objects look smaller than they are or vice versa
Treatment
- Monitoring: In some patients it resolves spontaneously.
Otherwise, a range of drugs might be
- Anti-inflammatory corticosteroids
- Laser Therapy: In rare instances, laser therapy can be
administered to scad leaking blood vessels.
6. Uveitis
Inflammatory disease that involves the uvea as the middle
layer of the eye, and thus includes the iris and ciliary body and chorioedema.
This if not treated affects the retina and results in loss of vision.
Causes of Uveitis
- Uveitis can result from autoimmune condition, infections,
and toxins exposure.
Symptoms:
- Eye redness
- Pain and photophobia
- Blurred vision
Treatment:
- Corticosteroids: Inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: In case of severe condition or if
it is autoimmune in etiology.
- Surgery: In a few cases due to complications.
7. Retinal Vein Occlusion
Retinal vein occlusion is a disorder whereby any of the many
retinal veins are thrombosis and become leaky, swollen with small hemorrhages
and sudden blindness.
Types:
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO): Central vein of the
retina is involved
- BRVO: One of the branches of central vein is involved
Symptoms:
- Abrupt vision loss in one eye
- Blurry or distorted vision
- Altered color vision
Treatment
- Anti-VEGF injections to reduce edema and hemorrhage
- Laser treatment in case of complications
- Comorbidity like disease management (e.g. diabetes,
hypertension)
Prevention of Diseases affecting the Retina
Indeed, the majority of the diseases are no preventable but simple alteration of some of the life styles and periodic general health checkup may reduce the likelihood of disease.
- Regular eye checkup can detect problems at an early stage,
thereby preventing the loss of vision.
- Chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and others can
be controlled to avoid complications.
- A healthy lifestyle will include a well-balanced diet,
regular exercise, and avoidance of smoking for the eyes.
- Protect Your Eyes: Wear sunglasses for protection from the
UV rays; protect yourself in any type of activity that damages your eyes.
Conclusion
Most of the Retinal diseases can be related to severe conditions; in any case, and they are leading to major and serious consequences to vision and overall quality of life. The capability to determine the different kinds of retinal diseases, including their symptoms and the appropriate treatments, makes much earlier detection and effective management of such problems possible which can even include prevention or reduction of risk for loss of vision.
If you are having the above symptoms of retinal
diseases, you should approach a professional eye doctor and get an excellent
evaluation and subsequent attention before it is too late.
Please book an appointment with the Best Eye Specialist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your disease.