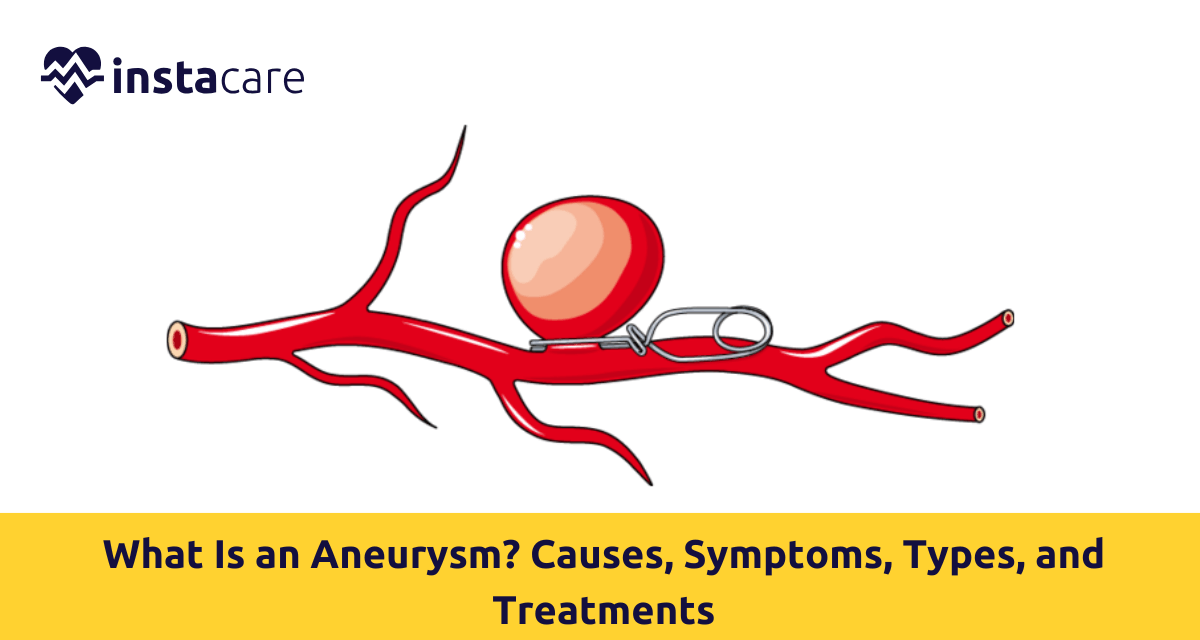
What is Aneurysm?
Various Types of Aneurysm
- Brain Aneurysm: A Brain aneurysm or cerebral aneurysm is a cerebral artery aneurysm. Rupture results in subarachnoid hemorrhage, stroke. It is an emergent illness, and when left untreated, will kill or cripple the brain within minutes.
- Aorta Aneurysm: An aneurysm of the aorta is an abdominal illness, the aorta a large artery that passes through the belly. Ruptured, spasmodic hemorrhage occurs throughout and will most likely be fatal unless treated right away.
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm: Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms are chest thoracic aortic aneurysms, arm and leg peripheral aneurysms, and cardiac ventricular aneurysms. They are similar in sign and risk, but most likely to rupture and cause devastating harm.
Some Important Causes of Aneurysm
- High Blood Pressure: Immediate cause is a rise in high blood pressure putting more stress on the walls of the arteries so that they contract and become smaller in the long run.
- Atherosclerosis: The second factor of huge value giving rise to it is atherosclerosis or deposits in the arteries. Atherosclerosis has a tendency to make the walls of blood vessels weak with the lapse of time.
- Genetic Factor: There is also a genetic factor. Some people are at greater risk due to family history, especially for cerebral aneurysms. Connective tissue disease such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome will also weaken the vessel wall.
- Injury or Infection: Traumatic injury, infection, and congenital disease are some others.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is also a major risk factor because it is harmful to blood vessels and leads to atherosclerosis.
View More: 10 Rarest Disease In The World
Important Symptoms of Aneurysm
- Brain Aneurysm: Symptoms of brain aneurysm would include worsening and acute headache (worst headache ever), change in vision, stiff neck, nausea, photophobia, and loss of consciousness. These are the most ominous symptoms indicating impending rupture.
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: Abdominal aortic aneurysm can lead to pulsation over the region of the belly, dull and long-standing pain, or backache and abdominal pain. On rupture, signs will develop very early dizziness, tachycardia, and loss of consciousness because of the decrease in blood in the body.
Top Aneurysm Risk Factors
- Age: The risk increases exponentially after the age of 60.
- Gender: Abdominal aortic aneurysms are found in men more so, but females have a higher chance of developing complications if brain aneurysms do rupture.
- Family History: The genetic illnesses may predispose the patient to brittle vessel walls.
- Smoking: causative cause of titanic power and bursting aetiology.
- Hypertension: Cumulative repetitive high-pressure strain on artery wall which continues to function over an extremely long duration.
- Chronic disease: like atherosclerosis, leading to artherosclerosis and loss of elasticity.
Effective Treatment Options for Aneurysm
- Surgical Clipping: Where treatment must be performed as soon as it can be, the most sought-after of the two treatments is surgery. In surgical clipping, a metal clip placed where an aneurysm occurs prevents blood flow from entering an aneurysm. Treatment in cerebral aneurysm is more sought after and entails an open procedure.
- Endovascular Coiling: Minimally invasive endovascular coiling is insertion of the catheter through the blood to the aneurysm site. Coils are implanted to initiate clotting and cut off the blood flow to the aneurysm. The procedure is mostly the best treatment since it has low recovery time as well as fewer risk factors.
- Open-Abdomen Surgery & Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR): For an aneurysm in the belly aorta, open-abdomen surgery or endovascular aneurysm grafting with an artificial graft inserted to support the wall of the aneurysm might be the solution.
Learn About Aneurysm Prevention
- Smoking cessation is likely to be the sole most crucial step towards its prevention. Smoking cigarettes not only leads to the development of an aneurysm but also provides a higher degree of vulnerability to rupture.
- Strict low-fat and saturated-cholesterol diet with other heart healthy foods to prevent atherosclerosis. There is frequent care with caution, particularly in familial or genetic risk. These are follow-ups for screening in aneurysm diameter follow-up in risk factor patients.
Conclusion