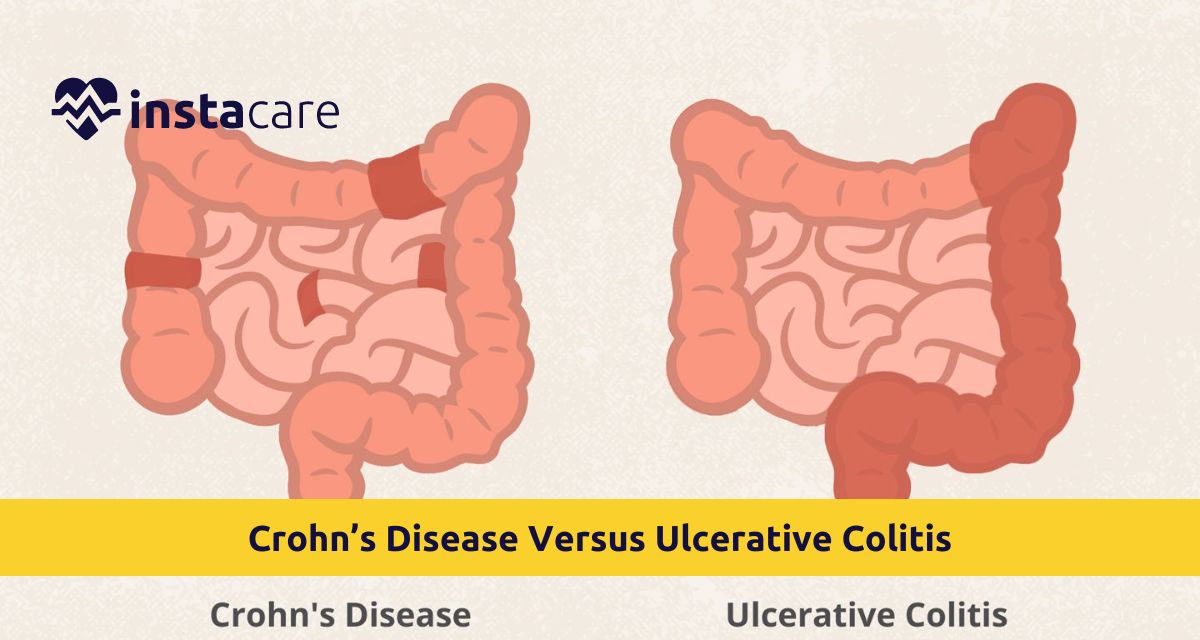
Since weeks now, you have had abdominal pain; you often sleep and are thin; and defecate frequently. What's happening? It could be an inflammatory bowel disease, but which one: Could it be Crohn’s disease or could it be ulcerative colitis? Just as an automobile company wants their car to be differentiated from their competitor’s car, doctors want to differentiate between two similar-sounding diseases.
There are two. Both are quite alike in many ways – in fact, as a chronic state of inflammation in your gastrointestinal tract. However, there are some differences that can cause variations in treatment. By the way, if you hear some people just say colitis, that has a limited meaning to it, that is not the same thing. It means inflammation of the colon. In the case of “ulcerative colitis” you get ulcers in the lining of your colon as well as inflammation.
Common Symptoms
The symptoms of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis (UC)
can be similar. They include:
- Abdominal cramps and tenderness
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- A feeling of urgency to pass a bowel movement
- You can feel your bowel movement was not complete
- You have rectal bleeding
- You had fevers
- You eat less than normal
- You lose your weight
- You feel tired
- Night sweats
- Disrupted period. You may miss them or know when they are
coming less predictably
- You cannot be suffering from all of those symptoms at the
same time.
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis or UC is one of IBD that affect large intestine including rectum and involves only the mucosa of colon. Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases as a group are evidenced by such manifestations as cramp-like abdominal pain, bloody diarrhoea, and rectal pain with the impression of defecation.
This disease can be mild for some but rather seriously
impairs their quality of life when it flares up badly. No known causes have
been reported for ulcerative colitis, although many reasons have been believed
to intermingle in a harmonious outbreak to cause the disease: genetic,
environmental, and immune factors.
What is Crohn's Disease?
The other sort of IBD is Crohn’s disease and it often occurs anywhere in the gi tract; however, it mainly impacts the end of the small bowel known as the ileum, and the beginning of the large colon known as the cecum Here, unlike ulcerative colitis, the layers of inflammation in the bowel wall of Crohn’s disease can extend through the entire depth.
The common signs of this illness are fever, weight loss,
diarrhea that can have a bloody stool, fatigue and stomach ache. Some of the
complications may include; fistulas, strictures and malabsorption with
malnutrition. The development of Crohn’s disease has not been fully determined
but its risk factors have not been established although it is known to be
caused by a combination of genetic, immune functions and environmental factors.
Cures are hence made with assistance from endoscopies, imaging tests, and a
biopsy. Some of the treatment involves avoiding inflammation through certain
medications, change of diet and where severe cases are involved surgery in
remove of regions in the intestine infected with it.
Crohn's Disease Symptoms
Symptoms of Crohn's disease disappear and have their up days and downs. However, once developed, symptoms may initially be gradual in nature before becoming mild or severe in character. Other symptoms that a patient with Crohn's disease may present other than abdominal pain include;
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Tiredness
- Bleeding from their stool
- Sore mouth
- Crohn's disease is related to, or can predispose many other
medical conditions. Among them include:
- Anemia
- Kidney stones
- Skin and joint inflammation
- Chronic malnutrition
- Bowel blockages
- Blood clotting
- Colon cancer
Ulcerative Colitis Symptoms
Common ulcerative colitis symptoms include:
- Rectal pain and bleeding
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Trouble going to the bathroom
- Dehydration
- Fever
- Complications of ulcerative colitis include:
- Severe bleeding
- Risk of colon cancer
- Osteoporosis
- Swollen or damage to the colon
Treatment of Crohn's Disease
Of all the stages inherent in the development of the
diseased condition, the most crucial is the identification stage. The current remedy for the diseased state associated with Crohn’s disease is still pending
but prevention or controlling of this disease has a lot to do with limiting the
occurrence and the intensity of the symptoms. The medicines that have been
managed include corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and antibiotics.
When the signs and symptoms cannot be controlled by
medicines and diet, surgery is used in an attempt to reduce the impact. Surgery
for Crohn’s disease neither cures it but instead functions to take out diseased
parts in the gastrointestinal tract.
Ulcerative Colitis Treatment
Crohn’s disease treatment essentially does not differ from
ulcerative colitis. Drugs would be similar, yet there would be a difference in
the drug response for Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
But there are surgical solutions and these remove colitis as
a condition altogether. That is one of the major differences between the
treatment options for both diseases: Of these operations, all are called
colitis though all of them involve pulling out the entire colon to cure the
disease.
Living with Crohns Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
Both can be severely debilitating to live with as they can
involve many parts of one's life. There is a need for a multidisciplinary
approach for best care of the symptoms and thus a good quality of life.
Diet and Nutrition
An IBD patient requires a healthy diet. Even though the
needs vary from one person to another, an overall general level of dietary
education may include the following:
- Hydration: Fluid intake must be ensured, especially during
diarrhea.
- Restrict Trigger Foods: Identification of foods that are triggers for the symptoms is required. In many cases, it may involve
milk products, greasy foods, or spicy food.
- Supplementation: Nutritional supplementation may also be required as it may not take in the required nutrients since the affected area
is not normal.
Stress Management
Stress increases the symptoms of both Crohn's and ulcerative
colitis. Stress can be managed through
Mindfulness and Meditation
The levels of stress can be reduced with these techniques.
Yoga and Physical Activity
Regular exercise in general can promote wellness.
Support Groups
Discussion with fellow patients who have the same diagnosis
may comfort the patient or, at least, provide some guidance
Follow-up care and Medical Care
Regular visits to your healthcare provider are part of
managing the illness. Control of your symptoms and appropriate changes in
treatment decrease flare-ups and complications.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis helps diagnose and cure the person properly suffering from this. Though they fall in the same category of inflammatory bowel diseases, the disease conditions are different regarding characteristics, signs, and treatment plans. Patients should be referred to medical advice whenever signs of IBD manifest for proper management and care. Correct strategies can help patients overcome their conditions to lead happy and healthy lifestyles.Please book an appointment with the Best General Physician in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your disease.