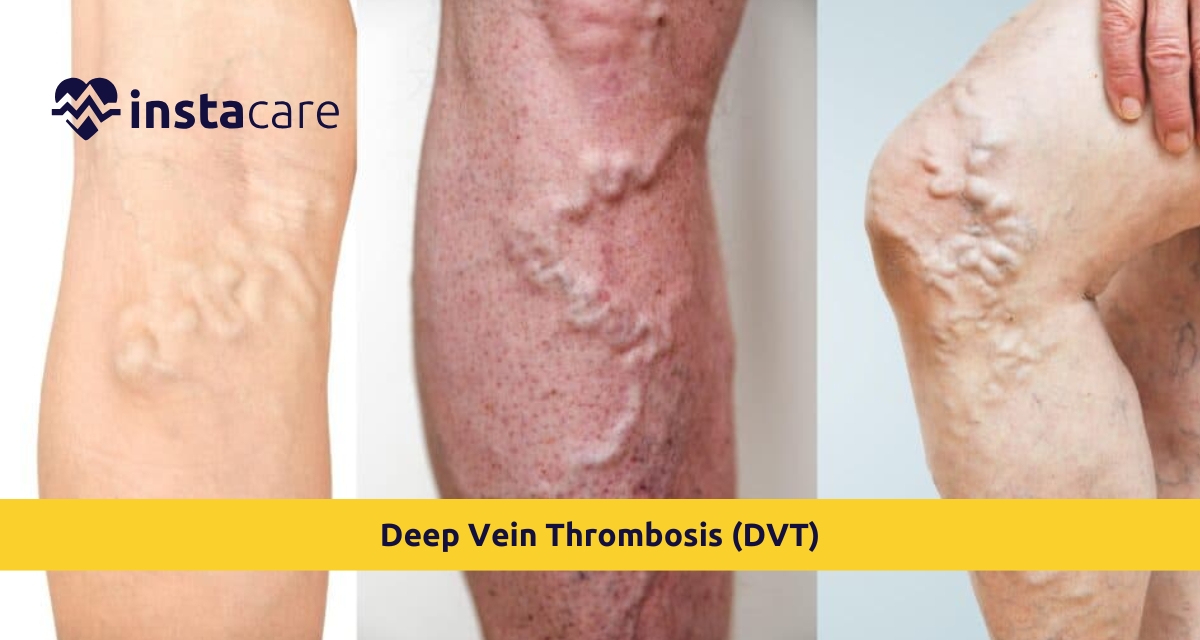
As its name suggests, Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is an absolute bane: a clot occurs inside deep veins, generally in the legs. Such a condition would naturally call for some study into Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and its prevention and management. This article thus covers the disease itself, its symptoms, etiologies, treatment, and DVT prevention. These sickening solvent-like malignancy conditions will comprise this article's subject matter.
DVT Explained
Deep vein thrombosis involves clot formation within a deep vein. More typically, this occurs at the lower extremities. A dislocated blood clot that blocks pulmonary artery flow results in pulmonary thromboembolism, which becomes the worsened complication. The combination of active symptom identification and appropriate medical care typically prevents the patient's condition from feeling dangerous effects. DVT is commonly due to prolonged immobility, such as during long airplane or car trips, followed by extended recuperation periods where the individual lies flat on their back.
Symptoms of DVT
Symptoms may differ depending on whether or not someone has DVT. Some may show no symptoms at all. Swelling occurs in just one leg and is generally accompanied by pain that resembles a cramp. The skin feels warm or hot, and changes or redness may appear around the area. These signs and symptoms warrant emergency hospital treatment because timely surgery would significantly reduce the dangers of complications from DVT.
DVT Causes
There are many DVT causes, such as long immobility periods, injured veins, prior medical conditions, and hormonal influences. Long seated behind the desk or standing in one position evokes inactivity and slows down the blood: this is the risk for clot formation: Prolonged immobilization. Moreover, an injury may also occur to the veins through surgery or trauma, making them susceptible to clot formation. Medical conditions such as
cancer or heart disease would increase the chances of the person developing DVT. Also, higher levels of hormones due to DVT in pregnancy or hormonal therapy replacement can be a risk factor for DVT.
Risk Factors for DVT
One could take preventive steps with this knowledge concerning risk factors of Deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Important risk factors include age, obesity, family history, and smoking. Age-related DVT risk factors go up, beginning from the early 60s, with gradually increasing pressure due to overweight veins creating difficulty for blood to flow. A family history of DVT or clotting disorders would also add to the risk. Smoking messes up blood circulation, and this" interference could just tilt the odds favorably for DVT formation."
Signs of DVT
Prompt recognition of Signs of DVT and symptoms will by itself lead to prompt intervention. Besides the significant symptoms known, an exaggerated degree of discrepancies in one leg swollen compared to the other aggravated by standing or walking are painful when standing or walking. Increased warmth in the area may also indicate a DVT. If any indications are present, take the person for medical evaluation as soon as possible to avoid further complications.
Diagnosing DVT
In most cases, DVT is diagnosed from different modalities: with the physician in terms of physical review and correlating DVT symptoms against medical history to rule out possible occasions of DVT. Ultrasound is a mainstay in investigations into blood flow and clot detection within veins. Another adjunct investigation is the D-dimer assay, to detect a particular substance released when a blood clot dissolves in a patient's body. Any of these three could definitely help to confirm or reject the presence of a DVT blood clot and what could be the next step in treating it.
DVT Treatment
DVT treatment aims to arrest the clot's propagation and reduce complication chances. Anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and compression stockings comprise the treatment plan. Anticoagulants, popularly known as blood thinners, prevent new clots from forming. Sometimes new clots can also be prevented by thrombolytic agents that may also dissolve clots. Compression stockings would help lessen DVT discomfort by preventing swelling and increasing circulation through your legs.
DVT Surgery
In this case, DVT surgery is offered to some patients to help dissolve blood clots in a DVT case. The surgical treatments involve thrombectomy for systematic blood clot removal or inferior vena cava filter placement for clot interception. These surgical interventions are performed in emergencies requiring urgent intervention to stop complications from developing.
Medications in DVT Treatment
The primary intervention method in treating deep venous thrombosis depends on the necessary drugs. The most commonly prescribed medications among anticoagulants are Warfarin and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). Warfarin was an oral medication that could be bought without a prescription until DOACs entered the market with their similar oral mechanism but dispensing with regular testing needs. The health care provider will determine which would be more useful based on your situation, medical history, and general health.
Compression Stockings in DVT
Compression stockings are the most effective method of non-invasive management of DVT. Apply pressure to the aimed toes to promote blood movement, relieve swelling, and eliminate stagnation. Compression stockings are usually prescribed to patients with risk factors or recovering from DVT. Wearing compression stockings would contribute to treating the symptoms and serve as part of a global program to improve the well-being of your legs.
The occurrence of DVT typically happens during pregnancy because hormonal changes combined with vein pressure increase. All pregnant women must thoroughly understand this medical subject and consult their healthcare providers about disease prevention methods. These are compression stockings or anticoagulant therapy in extremely high-risk conditions. All pregnant women should be encouraged to continue being active, be up and about, and keep from being immobile as a preventive measure for DVT.
Prevention of DVT
Prevention may become vital because not everyone is vulnerable to stasis. Almost all of it is keeping the body active.
Hydrated and, the most important of all, do not remain immobile for long periods. Physical activity enhances circulation and drastically lowers the possibility of clotting. With highly hydrated blood, smooth flow occurs. Taking a break from long-distance travel or sitting could also help.
DVT Complications
If left untreated, an individual can suffer life-threatening DVT complications such as pulmonary embolism, which heads into the lungs, or post-thrombotic syndrome; failure to detect and treat these successfully exposes the patient to unsavory outcomes. The most threatening conditions in the event of death or threatening life are pulmonary embolism and DVT when a thrombus from any part of the body invades the lungs and obstructs the flow of blood.
Those who pass DVT can look forward to having post-thrombotic syndrome, which leads to chronic pain and swelling of the legs. Early DVT diagnosis and management could avert the adverse effects of these complications, as has been documented in patients aided by DVT.
Conclusion
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is serious and should be understood better by people so that they can take rapid measures in the event of a medical emergency. Symptoms, causes, and preventive measures regarding such a terrible condition can thus be identified and reduced, ensuring that people do not have unexpected experiences with it but get quick treatment when necessary.
The suspicion of DVT should therefore lead one to seek immediate health care provider assessment and management needs. DVT is also very critical to understand as well as necessary in itself speaks a great deal about how it could play a role in your well-being.
Please book an appointment with the
best General Surgeon in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find the verified doctor for your disease.