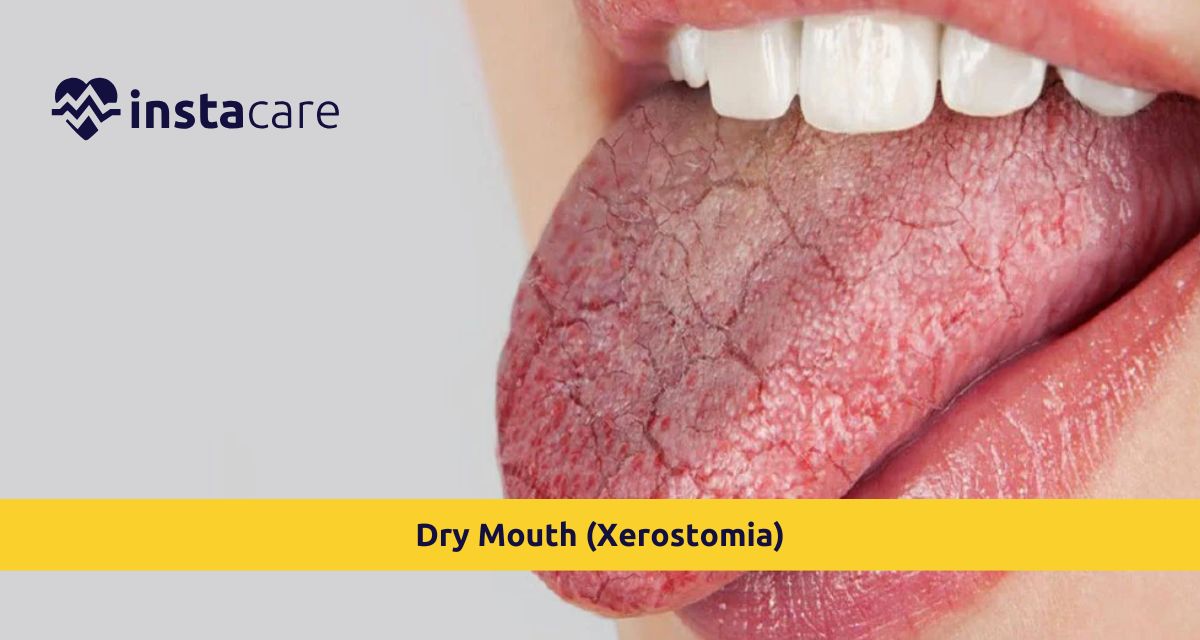
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) is less saliva secretion from the glands, hence creating discomfort and possibly complications in the oral cavity. Saliva plays a great role in digestion, as well as defense and integrity of the oral environment. When saliva production reduces, chewing, swallowing, and speaking become nearly impossible. Saliva lubricates mouth acids for protection against infection and cavities to the teeth and gums. Without it, food and bacteria accumulate inside the mouth, causing aggravation.
What is Xerostomia?
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) is an at-any-age illness but one of
increasing incidence in the aged. It is a symptom and not a disease of an
underlying disease or a medication side effect. Chronic or acute, it varies as
to the etiology. It is enabling an everyday aspect of life that is very
disturbing, warranting the treatment to commence as early as possible in
patients with chronic xerostomia.
Causes of Dry Mouth
Headaches are among many Causes of Dry Mouth, including the following:
- Drugs: Diuretics, antihistamines, and antidepressants tend
to reduce saliva secretion.
- Medical Conditions: Decreased salivation may occur in
Sjögren's syndrome, diabetes, and HIV/AIDS.
- Dehydration: When there is not enough fluid intake, saliva
production decreases.
- Lifestyle Habits: Coffee, alcohol, and tobacco can cause dry
mouth.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation for head and neck cancer can
leave patients with a permanent injury to their salivary glands.
- Nerve Damage: Damage of nerves either due to head or neck injury or surgery causes one of the causes of dry mouth.
Symptoms of Dry Mouth
Symptoms of Dry Mouth are often present in:
- Sticky, dry sensation in the mouth
- Constant feeling of thirst
- Trouble chewing, swallowing, or speaking
- Dry, sore throat
- Chap lips
- Bad breath odor
- Hoarseness and nasal dryness
- Greater susceptibility to oral infection like thrush
How to Treat Dry Mouth?
If you have Dry Mouth (Xerostomia), several things can be done to know How to Treat Dry Mouth:
- Drink water whenever needed throughout the day.
- While chewing gum (sugar-free) enhances the tactical
movements of salivary glands to release more saliva.
- An armchair humidifier intends to facilitate proper humidity
in the air.
- Do not use mouthwash containing alcohol.
- Cut down on drinks that is dehydrating, like caffeine or
alcohol.
- Sucking on sugar-free candies or popsicles will help in
keeping the mouth moist.
- In this case, saliva substitutes and prescription and
over-the-counter medication stimulate saliva.
- Oral hygiene must be practiced to eliminate dry mouth conditions that lead to dental problems.
Dry Mouth & Its Impact On Various Health Conditions
Dry Mouth and Dehydration
A Dry Mouth and Dehydration are twins. The more dehydrated a person is, the less saliva is produced, leading to a dry mouth. There should be adequate hydration to prevent such dry mouth conditions. Given below are some excellent tips that will help keep up that hydration:
- Eight glasses of water daily.
- Eat hydrophilic fruits, such as oranges, watermelons, and
cucumbers.
- Limit your salt intake so it will not cause dehydration in
your body.
- Drink water-based decoction or herb tea.
View More: Mouth Ulcer: Causes, Types, & and Treatment
Dry Mouth and Bad Breath
The effects of Dry Mouth and Bad Breath are reduced saliva to eliminate food particles and bacteria. This is cause for odor and increased risk for gum disease and tooth decay. How to fight dry mouth bad breath:
- Brush and floss your teeth every day to eliminate food
particles.
- Rinse with an alcohol-free mouthwash.
- Use saliva to moisten your mouth and rinse your mouth
frequently.
- Chew sugarless gum to stimulate saliva flow.
Dry Mouth and Diabetes Relationship
Dry Mouth and Diabetes Connection is hand in glove. Water evaporation is stimulated because of high blood glucose and consequent reduced salivation. Diabetic patients also get infected, and hence, the worst one is dry mouth. What is diabetes dry mouth treatment:
- Regularly monitor blood sugars.
- Use frequent water and mouth hygiene.
- Utilize saliva substitutes when necessary.
Dry Mouth and Aging
As an individual becomes older, senility and dry mouth are more likely to result from reduced salivation. Certain medications and diseases in older participants bring about Dry Mouth and Aging. Regular visitation will prevent the symptoms. The elderly are assisted by:
- Excellent water intake throughout the day.
- Consumption of artificial saliva product.
- Evaluation of drug side effects and alternate therapy recommendation from the physician.
Xerostomia and Oral Disease Risk
Xerostomia and Oral Health Risks are synonyms. Due to decreased secretion of saliva, the mouth is predisposed to being more susceptible to:
- Increased formation of plaque
- Gum infection and tooth caries
- Fungal infections like oral thrush
- Teeth sensitivity and dental wear and tear
Foods That Should Be Avoided for Dry Mouth Relief
Some foods can trigger Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) symptoms, making a person suffer and aggravating oral complications. Thus, it can be advised that, for those concerning food consideration, Foods to Avoid for Dry Mouth Relief of the following sets:
- Salty foods tend to dehydrate; therefore, these will worsen
dry mouth symptoms.
- Spicy food can irritate the mouth, causing extra discomfort
when saliva production is already low.
- Sugar may lead to tooth decay and gum diseases since
bacteria thrive on sugar.
- Alcohol and caffeine have a dehydrating effect and hinder
saliva production.
- Acidic foods, e.g., citrus, may do some damage to the mouth,
thereby further increasing the pain or irritation or causing the formation of
an ulcer.
- Dry or rough foods become even harder to chew and swallow
when there is little saliva, such as crackers, toast, and chips.
- Acidic sodas, thus more drying to the mouth.
Prevention of Dry Mouth
How to Prevent Dry Mouth. The answer is adopting healthy habits:
- Drink plenty of volumes of water in a bid to achieve good
hydration levels.
- Brushing with fluoride toothpaste to avoid cavities.
- Cut or avoid caffeine, alcohol, and smoking.
- Following routine oral hygiene practices to avoid bacteria
buildup.
- Food chewing that naturally activates saliva, including
apples, carrots, and celery.
- Occasional visits to the dentist for oral checkups and professional guidance.
Night Dry Mouth
Dry Mouth at Night is experienced by all, usually caused by sleeping with the mouth open. Night dry mouth can be reduced by adding a humidifier, taking liquids during the day, and avoiding late-evening consumption of caffeine. Some additional tips are:
- Sleeping with a nasal strip to breathe nasally.
- Keeping water at hand to keep you hydrated all night long.
- Priming with a moisturizing oral spray before sleep.
Conclusion
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia) is a fairly common problem that can theoretically affect oral health, digestion, and general health. Early detection of symptoms and their etiology underlies the prevention of complications. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, drinking plenty of water, and adopting lifestyle changes are essential in providing the best treatment and compatibility of life to the dry mouth sufferer. Controlling the disorder could prevent long-term complications to oral health and promote comfort.
Please book an appointment with the best General Physician in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find the verified doctor for your disease.