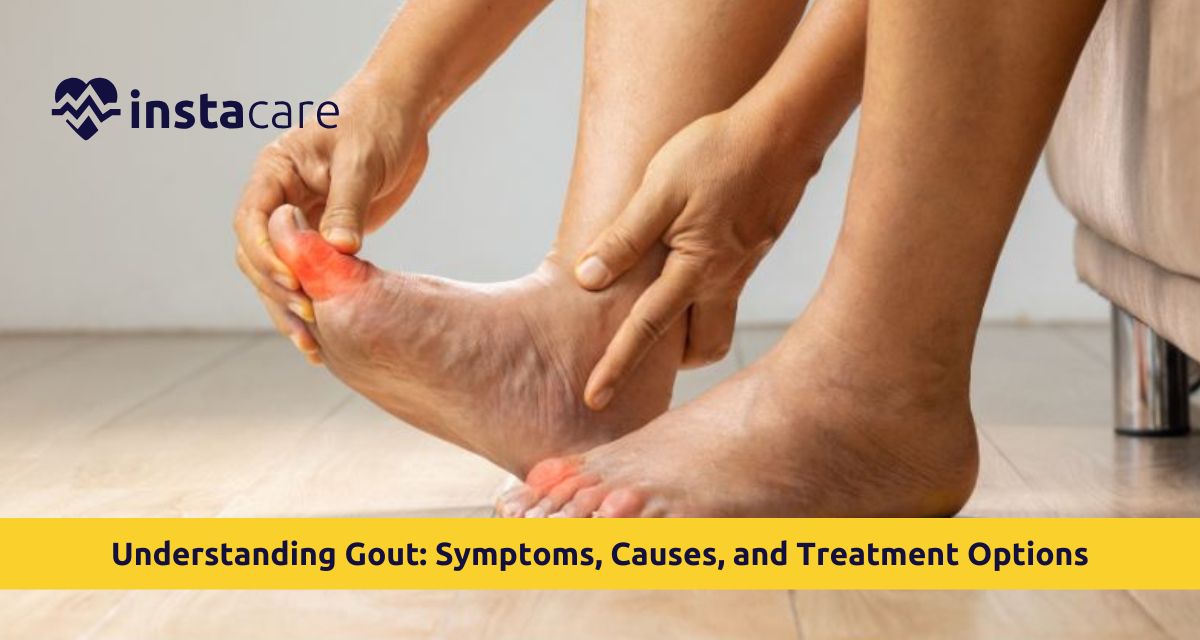
Inflammatory arthritis, commonly known as gout, causes sudden pain in millions of patients worldwide. Joint crystals form when uric acid crystals settle within the blood and then accumulate in the body's joints, causing burning discomfort and severe pain, and swelling with redness.. Uncontrolled gout resulting from episodic flare-ups and pyogenic joint inflammation can damage life quality through its characteristic manifestations. Treatable gout requires an early and accurate diagnosis in newly diagnosed patients, as well as optimal treatment approaches.
What is Gout?
It is urate crystal deposition arthritis and occurs most commonly on the great toe. They are deposited crystals that happen when there is an excess of
uric acid in the blood, a by-product of purine breakdown in foods and drinks.
Gout is unique among other types of arthritis in that it is characterised by acute, spontaneous pain. It strikes at midnight and is so painful that even having a bed sheet on the gout-affected joint is intolerable.
Chronic Gout refers to recurrent attacks resulting in chronic joint destruction. Urate crystals can ultimately deposit as nodules called tophi, resulting in chronic pain and deformity. Chronic gout is managed by the constant intake of drugs lowering uric acid levels and by accepting the usage of lifestyle changes.
Causes of Gout
Causes of Gout are primarily the overproduction of uric acid, or hyperuricemia. It may be due to:
- Increased secretion of uric acid by the body
- Reduced functioning of the kidneys to eliminate uric acid
- Elevated purine diet (in red meat, fish, and beer)
- Genetics, gender (greater in men), obesity, and other disease conditions such as hypertension or kidney disease are also risk factors for gout.
Foods That Cause Gout
Foods that Trigger Gout are commonly high in purine. Some of which include:
- Red organ meat and organ meat (kidney, liver)
- Shellfish (lobster and shrimp)
- Beverages of alcohol, primarily beer
- Honeyed beverages and high-fructose corn syrup
- Elimination or reduction of such food might prevent attacks as well as lower uric acid levels.
Gout Symptoms
Early recognition of Gout Symptoms is imperative for effective treatment of gout. Most common symptoms are:
- Excruciating pain in the joint, specifically the big toe
- Redness and inflammation above the involved joint
- Chronic pain in spite of the alleviation of acute pain
- Limited range of motion during and between flares
- Exacerbations, or flares, for days, and will most likely return unless under treatment for gout.
Gout Diagnosis
Doctors use three methods to diagnose Gout: physical examination and medical history review, and laboratory test assessments. Doctors check the synovial fluid of the joint to verify the existence of uric acid crystals. Uric acid measurement occurs through blood testing procedures. Medical professionals use either ultrasonography or X-rays as diagnostic tools to eliminate other joint diseases.
Treatment for Gout
There are Gout Treatment Options that can remove and heal symptoms:
- Medications
- Painful medications (NSAIDs, or Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
- Colchicine to counteract swelling
- Corticosteroids to alleviate acute pain
- Uric acid-lowering medications like allopurinol or febuxostat
Lifestyle changes
- Maintenance of optimal weight
- Abstinence from alcohol and refusal of high purine foods
- Ingestion of adequate fluid for the removal of uric acid
- Attacks and degree of uric acid-dependent individualized treatment according to the patient's status.
View More: Best Diet for Gout What to Eat What to Avoid
Gout Pain Relief
Efficiency in Gout Pain Relief is of paramount importance at the attack. The interventions recommended are:
- Application of ice packs to manage swelling
- Rest and elevation of the affected joint
- Compliance with taken anti-inflammatory drug
- Ingestion of ample water to facilitate uric acid flushing
- Prompt treatment can work magic in reducing the time and severity of symptoms.
Gout & Its Impact On Physical Health
Gout and Uric Acid Level
Gout and Uric Acid Levels are a pair. For everyone, the uric acid must be below 6 mg/dL. As levels creep higher above that threshold, crystals develop and are able to block up joints. Blood tests are often necessary to monitor them closely and prevent flare-ups.
Gout vs Arthritis
Gout vs. arthritis can be confusing, but while both diseases involve joint pain, they are triggered and occur in different ways. Gout usually arises as a new, severe pain in one joint, often the big toe, on the basis of uric acid crystals. Other types of arthritis, like osteoarthritis, however, develop slowly and can affect multiple joints symmetrically.
Gout Flare-Up Management Treatment
Treatment of Gout Flare-Up Management is indicated to prevent recurrence and reduce severity.
The following are some of the emergency actions one can adopt during a gout attack:
- Hydrate well: Take plenty of water to aid uric acid elimination.
- Avoid alcohol intake: Especially beer and liquor that raise uric acid.
- Treat early: Start anti-inflammatory medications as soon as the attack begins.
- Rest the joint: Avoid loading the affected joint.
- Ice pack: Apply an ice pack over the joint for 20 minutes, three or four times daily.
These measures in the early stages may curb the severity of attacks and hasten recovery at a faster rate.
What Includes Gout Diet Plan?
Gout Diet Plan should be adopted if the condition is to be managed. A balanced diet can help reduce uric acid levels and prevent frequent attacks. Incorporate:
- Low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese
- Cereals, whole grain
- Raw fruits and vegetables, especially cherries
- Coffee its uric acid-lowering benefits have been established by studies
- Water large amounts
- Avoid purine-containing foods, and maintain a healthy body weight.
What are the Risk Factors for Gout?
Understanding the Risk Factors of gout can help you take preventive measures. They include:
- Family history of gout
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Obesity
- Use of some drugs like diuretics
- Men between the ages of 30-50 years are at risk, but women become so after menopause.
Tips on How to Prevent Gout
Prevent the attacks from happening by implementing these Gout Prevention Tips:
- Maintain a balanced low-purine diet
- Drink enough fluids with at least 8-10 glasses daily
- Do not consume alcohol, particularly beer
- Maintain body weight to stay healthy
- Exercise, but do not tire during attacks
Preventive early treatment can considerably reduce the long-term impact of gout.
Conclusion
Gout extends beyond joint discomfort to manifest as a serious medical condition that can be dangerous for individuals unless they receive appropriate medical treatment. Patients enhance their ability to prevent and control their gout condition by studying its symptoms alongside risk factors, along with nutritional guidelines and suitable treatments. Medical professionals should combine lifestyle transformation with adjusted medication protocols to restore joint health and maintain patient quality of life in gout treatment.
Please book an appointment with the
best Rheumatologist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your disease.