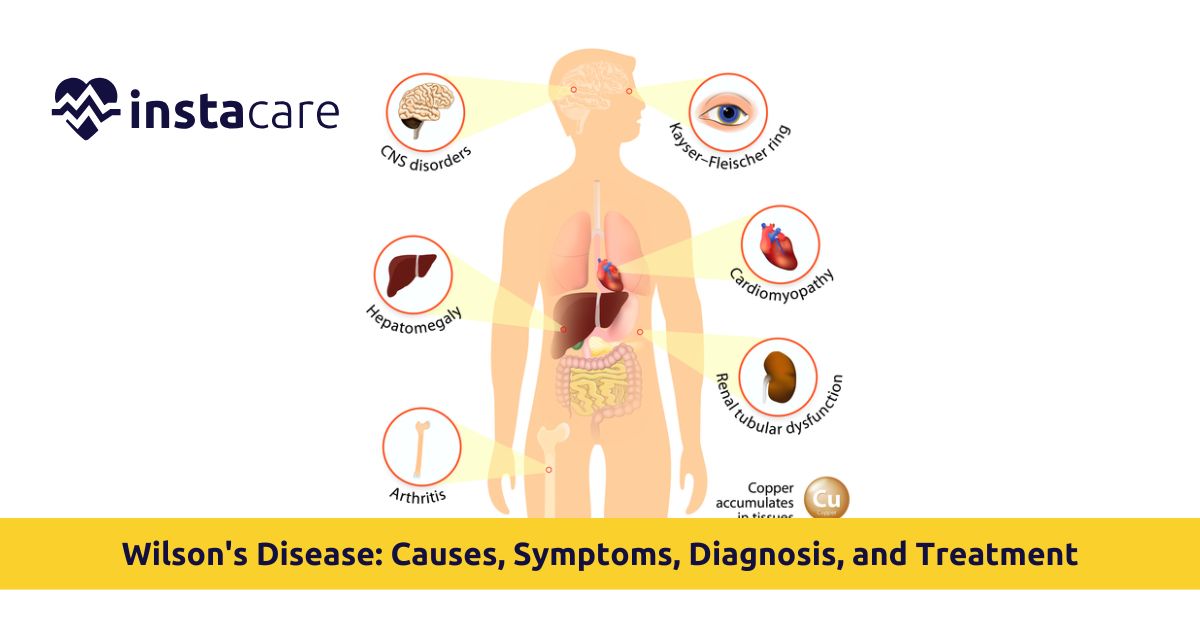
The illness occurs as a result of mutations in the gene that codes for ATP7B, the gene responsible for controlling copper transport across the body. When the gene fails to function as it should, copper is not being expelled from the body via bile as normal but rather is being kept trapped within tissues. Wilson's Disease occurs in about 1 individual per every 30,000 individuals worldwide and, if not treated, can cause potentially life-threatening complications.
Wilson's Disease patients can have an active and productive life if only they get diagnosed on time and treated appropriately. To learn more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, long-term management, and care tips, read this blog further.
Causes of Wilson's Disease
The gene disorder that causes Wilson's Disease is caused by a mutation of the role of the ATP7B gene mutation used in the elimination of excess copper from the body through the use of the liver via the bile. Without this gene in the disease, the copper accumulates in the other organs of the body such as the liver, brain, eyes, and kidneys and kills them.
Wilson's Disease is an autosomal recessive condition. Wilson's disease in children will need to inherit two genes for the condition-ones from each parent in order to present with the condition. Carrier individuals with one copy of the gene are not affected but will pass on the gene to their child. The. illness has a tendency to speak secretly during childhood or adolescence, and. signs do not materialize until copper accumulates to poisonous amounts, usually between the ages of 5 to 35.
Symptoms of Wilson's Disease
Wilson's Disease presentation is heterogeneous according to organs involved and severity of illness. Most common organs involved are liver and nervous system.
Hepatic Symptoms (Liver symptoms)
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowish color of skin or eyes)
- Abdominal or leg swelling
- Inflammation of the liver or hepatitis
- Enlarged spleen or liver
- Liver failure or end-stage cirrhosis
The above-mentioned signs and hepatic symptoms of Wilson's disease may be caused by other genetic liver disorders, so Wilson's Disease becomes challenging to diagnose during its early stages without the assistance of high-tech investigations.
Neurological Symptoms
- Shaking or tremor
- Muscle stiffness
- Gait or speech difficulty
- Mood change like depression, anxiety, or irritability
- Uncertain coordination and balance
- Slurred speech
- Drooling or dysphagia
These, in the absence of suspicion of neurological symptoms of Wilson's disease, will be mimicked by either psychiatric illness or Parkinson disease.
Eye Symptoms
A second extremely frequent and classical presentation of Wilson's disease eye symptoms (Kayser-Fleischer rings) is the development of Kayser-Fleischer rings, green or brown pigmented rings surrounding the cornea secondary to ocular deposition of copper. They are detected on slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy and are a helpful finding.
Diagnosis of Wilson's Disease
Wilson's Disease diagnosis is confirmed by imaging studies, laboratory studies, and physical examination. Early diagnosis of Wilson's Disease is necessary not to cause permanent alteration.
Blood Tests
- Decreased serum ceruloplasmin, copper-binding protein in Wilson's Disease.
- Abnormality of liver enzymes signifies damage to the liver.
Read More: Graves' Disease
24-hour Urinary Copper Test
It measures a 24-hour urine copper excretion. Elevated copper is an excellent marker for Wilson's Disease.
Liver Biopsy
Liver biopsy may be performed to measure copper actually. It is usually performed if all other tests are non-specific.
Genetic Testing
Wilson's disease and family screening is helpfull. Genetic test for mutation of ATP7B gene for diagnostic confirmation and can also be employed for screening of affected relatives by family screening.
Eye Checkup
Kayser-Fleischer ring is highly suggestive in Wilson's Disease, particularly in patients with neurological presentation.
Treatment Techniques
Wilson's Disease treatment is the depletion of body copper and prevention of re-accumulation. It is lifelong and follow-up.
Copper Chelation Therapy
Medications that chelate copper chelate copper and excrete it via urine.
- Penicillamine: First drug used widely, but fever or arthralgias as side reaction.
- Trientine: Administered if penicillamine intolerance in patients. Fewer side effects but dietary restriction strict.
These drugs function effectively to reduce overload of copper and enhancement of brain and liver functions in the long term.
Zinc Therapy
Zinc inhibits copper absorption from the intestine and induces excretion. It is usually given:
- As follow-up therapy following initial copper reduction
- To asymptomatic patients or as follow-up in the long run
Dietary Restrictions
The patients are discouraged from copper-containing foods such as:
- Shellfish
- Nuts and seeds
- Chocolate
- Mushrooms
- Organ meats (liver)
Even copper-free equipment employed for preparation and consumption water may be subjected to a test of copper.
Liver Transplantation
If the liver is severely damaged or any form of treatment medically fails, a liver transplant in Wilson's disease has to be done. It will then heal Wilson's Disease and save lives by substituting a faulty gene, ATP7B, with a good liver.
Prognosis and Long-term Treatment
Wilson's disease life expectancy is not different in a patient with Wilson's Disease with early treatment and ongoing management. However, follow-up and long-term management are needed to prevent the complications.
Key issues of management:
- Evaluation by a hepatologist or a neurologist serially
- Serial Wilson's disease test for liver function and copper studies
- Adjunct therapy and diet as advised
- Genetic counselling and screening of siblings and relatives
These patients who are treated prior to accumulating huge liver or brain damage can have normal, productive lives.
Conclusion
Wilson's Disease is not rare, but its impact is disastrous if not controlled. Awareness of causes, Wilson's disease symptoms, and treatment enable individuals and families to act early and be on the correct path. If you or your relative develops any symptom of liver disease or abnormal neurological finding, especially if you are an adolescent or child, see a doctor. Early detection will save your life. If you or your relative has been accurately diagnosed, treated by copper chelation therapy, and managed appropriately, Wilson's Disease can be disease-free.
Please book an appointment with the
best Neurologist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your disease.