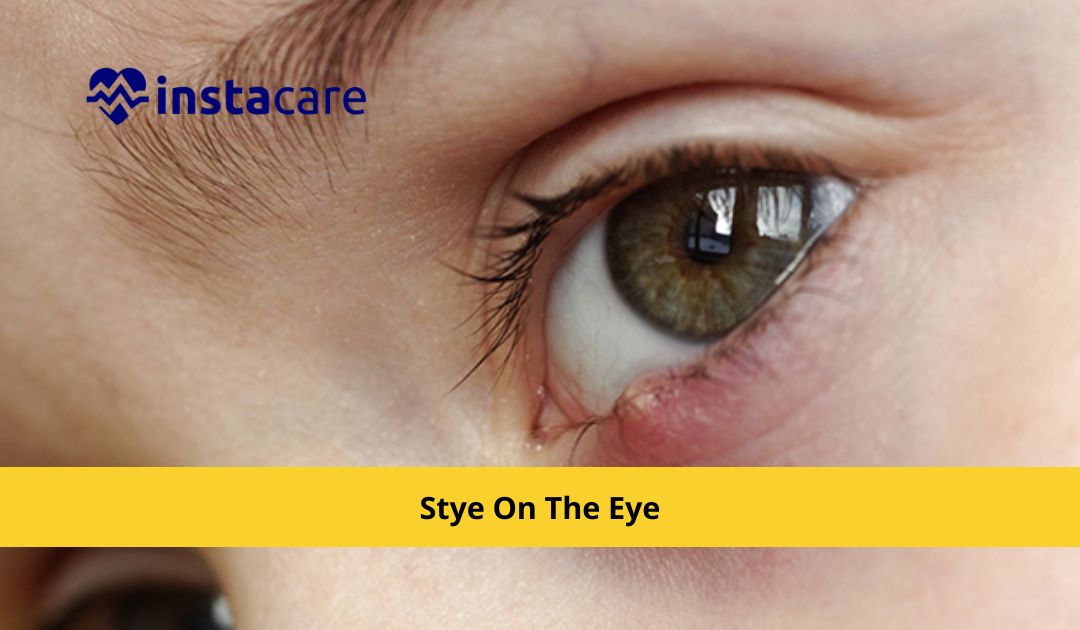
An infection caused by Staphylococcus bacteria results in an
inflammation of the eyelid known as a stye. Styes develop into a lump that
contains pus. Inadequate cleanliness when wearing contact lenses or cosmetics
is one of the causes.
An oil gland inflammation is called a stye. It also goes by "hordeolum" and is occasionally spelled "sty." The source of inflammation is a bacterial infection. Most cases of styes resolve in a week. Some folks could have symptoms that don't go away and need more care. The symptoms, diagnosis, home remedies, therapies, risk factors, and potential complications of a stye will all be covered in this article.
Signs And Symptoms To Be Aware Of
A stye causes a painful red swelling on the eyelid, which causes the eye to turn red. The mass frequently resembles a pimple or boil. Usually, styes affect both eyes at once. Typically, a person has one stye eye. However, one stye in each eye or multiple styes in the same eye is possible.
Additional signs of a stye could be:
- Some Tenderness
- Crusting of the margins indeed of the eyelids
- Some Burning sensation
- Itching indeed of the eye
- Experiencing Blurry vision
- Discharge indeed of mucus from the eye
- Light sensitivity
- Tearing
- Discomfort indeed when blinking
- The Feeling That There Is An Object In The Eye
Understand When To Seek Medical Advice?
A patient needs to consult a physician if:
- The condition lasts more than a week and causes eyesight
issues
- The eyelid or eye turns red; the swelling gets extremely
painful; it bleeds or spreads to other areas of the face.
Various Types Of Stye On The Eye To Know About
Most styes start outside the eyelid, where they can discharge pus and turn yellow. Certain styes indeed develop inside the eyelid, and they are typically more painful.
A stye can be classified into two general categories:
External Hordeolum
External styes appear along the outside border of the
eyelid. When touched, they may turn pus-filled, yellow, and painful.
The following infections have the potential to cause
external styes:
- Eyelash Follicle: The tiny openings in the skin where eyelashes grow are called lash follicles.
- Sebaceous Gland: This gland secretes sebum and is affixed to the lash
follicle. Sebum prevents the lash from drying out and helps lubricate it.
- Apocrine Gland: The apocrine gland also aids in keeping eyelashes from
drying out. The sweat gland drains into the follicle that holds the eyelashes.
View More: What Are the Flaxseed Oil Benefits For Eyes
Internal Hordeolum
Inside the eyelid is where the swelling appears. An internal
hordeolum typically hurts more than an exterior one. Doctors also know them as
internal styes, and their most common cause is a meibomian gland infection. The
secretion these glands produce contributes to the layer of film covering the
eye.
Furthermore, patients might have tearing, a burning sensation
in the eye, crusting around the edges of their eyelids, tingling in the
eyeball, sensitivity to light, and uneasiness while blinking.
Factors That Increase The Risk And Causes
Styes can occur at any age, although they are more prevalent in adolescents. The probability of getting stye can be raised by the following:
- Use makeup beyond its expiration date
- Not cleaning contact lenses before inserting them
- Not taking off makeup before bed
- Not replacing contact lenses without adequately washing
hands
- Poor nutrition
- Lack of sleep
Styes need to be more communicative, yet if somebody in the
house has one, different members shouldn't share face towels or washcloths. The
risk of cross-contamination is reduced when this sort of interaction is kept away
because the towels can contain microorganisms.
Styes can occasionally develop as a side effect of
blepharitis, an infection of the eyelids. A bacterial infection causes
blepharitis, although it can also sometimes be a side effect of rosacea, an
inflammatory skin disease primarily affecting the face.
Some Measures For The Treatment Of Styes
Most styes resolve all alone without the requirement for
clinical consideration. But, if the sore
spot is very excruciating, utilizing pain relievers could be advantageous. It
is prescribed to wait until the stye has completely vanished before using
lotions, contact lenses, or eye
cosmetics. Doctors also advise the following home therapies and remedies
Warm Compress
Doctors advise applying a warm compress instead of popping a
blister on oneself. A warm compress indeed applied gently to the eye may help
reduce discomfort and facilitate the release of pus. It shouldn't be too hot in
the water. One should use extra caution when administering the compress to
someone else to prevent overheating or applying excessive pressure.
Three or four times a day, the patient should apply the
compress to the eye for ten to fifteen minutes at a time. Once the styes
rupture, the symptoms usually get better quickly. The compress not only
relieves the pain, but it might also help the pus to go.
Antibiotics
The doctor could recommend topical antibiotic cream or eye
drops if the stye lasts longer than expected. A medical professional may
prescribe oral antibiotics if the infection extends past the eyelid.
More Treatments
In cases where an external stye is excruciatingly painful,
the physician may extract the closest eyelash and use a small needle to lance
it to remove the pus. Only a specialist should perform this surgery. A
physician might recommend a patient to an ophthalmologist or another expert if
their condition worsens.
Complications
Even though they are exceedingly rare, complications can
occasionally happen, such as:
Meibomian Cyst
A cyst of the tiny glands of the eyelid is called a
meibomian cyst. The glands around the edge of the eyelid release sebum. A
meibomian cyst might eventually arise from a persistent stye inside the eyelid,
mainly if it obstructs the gland. Treatment for this kind of cyst is simple and
efficient.
Preseptal Cellulitis
Cellulitis could happen if the contamination gets into the
tissue encompassing the eye. As a result of epidermal layer inflammation, the
eyelids swell and become red. Specialists utilize antibiotics to treat this
sort of disease. Even though these issues are possible, most stye instances
resolve independently with little help.
Conclusion
Styes are quite common and unpleasant, although they usually do not cause concern. Styes can lead to inevitable consequences, like developing a cyst or spreading the infection. Doctors can, however, manage both uncommon side effects. A stye can also occur due to certain factors, such as wearing particular cosmetics or getting too little sleep. Physicians advise patients with styes to treat the inflammation at home, but if the condition worsens, they may give antibiotics.
Please book an appointment with the Best Eye Specialist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find the verified doctor for your disease.