What is an EMG Test?
EMG test or Electromyography is a medical test conducted to test the health of muscles and motor neurons that regulate muscles. Motor neurons generate electrical impulses to stimulate muscles and EMG tests to estimate impulses so that muscle abnormality or nerve can be traced.
EMG is of inestimable value in neuromuscular disease diagnosis. Interpreting electrical impulses in a muscle allows physicians to rule out or confirm the entire gamut of nerve damage, abnormal muscle, and break-down disease in transfer between muscle and nerves.
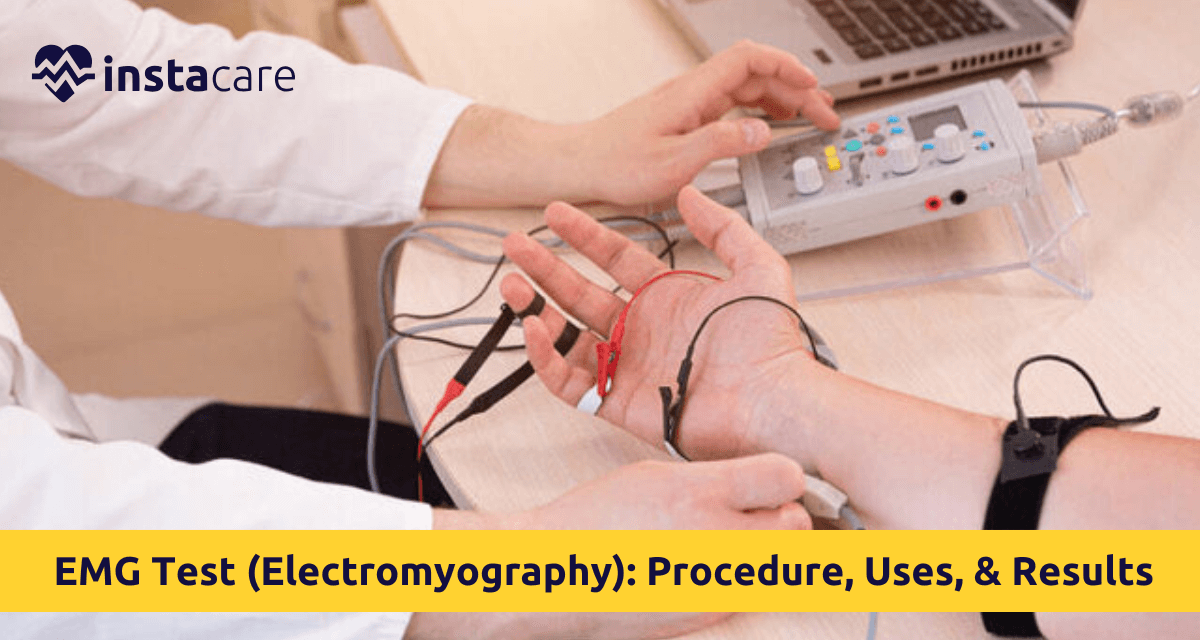
EMG testing involves placing tiny needles (electrodes) within the muscle and recording electricity at rest and with muscle contraction. Occasionally, the test is done with a nerve conduction study (NCS) to get a full picture of neuromuscular health.
Why is the EMG Test Done?
When is EMG test needed? EMG test is typically ordered when the patient feels numbness, weakness of muscle, pain, or tingling without a reason. The test identifies whether the problem is within the muscles or the nerve supplying them.
The most common situations for EMG test uses:
- EMG test for nerve damage to diagnose peripheral neuropathy
- EMG test for carpal tunnel syndrome (compression of the median nerve)
- EMG test for back pain due to pinched nerves or spinal issues
- EMG test for leg pain due to sciatica or due to compression of nerve roots
- EMG test for arm pain to determine whether it's cervical radiculopathy
- Disease of muscles such as muscular dystrophy or myopathy
- Motor neuron disease such as ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)
Most commonly, EMG test use is most appropriate when a patient presents with symptoms of defective muscles or nerves, locating the site of pain or mobility defect very specifically.
How to Prepare for an EMG Test?
Preparation results in precise results and a safe test procedure. Although EMG test preparation is minimal, repetition of these rules is essential:
Preparation guidelines
- Clothing: Loosen up, loose clothing that will not restrict movement into the test room will suffice. A hospital gown works best when it is finally time to get changed.
- Skin Care: Do not apply oil, lotion, or cream to your skin on test day as these will affect the electrodes.
- Medications: Let your doctor know if you're on medication, especially blood-thinners or acting-muscle medication. Do not cease taking medication on your own.
- Medical Devices: Let your doctor know if you're on a pacemaker or other electrical device implanted because some precautions will have to be taken.
- Dining: You will usually be allowed to eat beforehand, except for what your doctor instructed otherwise.
Honesty regarding your disease history and symptoms helps the neurologist make the proper diagnosis.
EMG Test Procedure
The EMG test procedure is between 30-60 minutes long, depending on how many are being tested in a muscle and in a nerve.
You will typically be:
Initial Preparation:
You will lie down or sit back depending on what area is to be tested.
Your skin is ready, and the doctor can first do an NCS test by placing electrodes on your skin to check the reaction of a nerve.
Needle Electromyography (EMG) Insertion:
A sterile, thin needle electrode is inserted into every muscle.
The needle is able to measure electrical activity at rest and with.
Recording:
You are requested by the doctor to contract the muscle (e.g., curl arm or lift leg).
The sound of the electrical activity of the muscle is audible and is monitored on a screen.
Analysis:
The signals are used to calculate velocity and amplitude of electrical activity of the muscle and faults.
The procedure is usually safe and bearable. Even though the needle will be painful for a second, it is mild and temporary.
What to Expect After the EMG Test?
Most individuals are able to get back to their normal activities within a few minutes of the test.
Post-test follow-up and EMG test side effects:
- Mild soreness: Most commonly described is mild soreness or tenderness of the muscle at the point where the puncture is done by the needle.
- Bruising: Bruising is seen in some individuals, especially individuals who have thin skin.
- Downtime-free: Most patients may go back to their regular day-to-day activities without any downtime after the test.
- Pain control: Pain medicine Tylenol is also available for "as needed" use.
If there's persistent pain, swelling, or evidence of infection (abnormal), contact our doctor at once.
Reading EMG Test Results
The neurologist interprets an EMG test results by examining the pattern of electricity in your muscles.
Normal results:
- Do not have abnormal spontaneous activity during resting muscles.
- Have normal electrical responses during contracting muscle.
- Abnormal results are caused by:
- Nerve impairment such as neuropathy or radiculopathy.
- Muscle disease such as polymyositis or muscular dystrophy
- Motor neuron disease such as ALS
Recurrent tests or imaging (MRI, blood studies, or biopsy) can be recommended for diagnosis based on EMG reports.
Diseases Diagnosed by EMG Test
Other conditions of the neuromuscular system require more time for the EMG test to diagnose.
Those conditions are generally diagnosed:
- Neuropathy lying peripherally
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Radiculopathy (spinal nerve root pathology)
- Muscle weakness or myopathy muscle diseases
- ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis)
- Brachial plexopathy
- Herniated discs compressing nerves
- Sciatica
These tests help to have a good treatment plan, drug therapy, physical therapy, or surgery.
EMG Test vs Nerve Conduction Study (NCS)
While the EMG test (Electromyography) and the Nerve Conduction Study (NCS) are typically performed together, they serve varying purposes in Neurological testing EMG. The EMG test tests for muscle electrical activity and can detect muscle disorders or diseases of the nerves that regulate them. NCS, however, is used to quantify the speed and amplitude of impulses traveling through the peripheral nerves.
It is employed to identify nerve damage or impairment, such as that caused by carpal tunnel syndrome or peripheral neuropathy. Together, EMG and NCS provide a better comprehension of both muscle and nerve health, and enables physicians to establish the location and type of neuromuscular disorder.
EMG Test Price in Pakistan
Approximate price range:
- Simple EMG test: PKR 6,000 to PKR 12,000
- EMG with NCS: PKR 10,000 to PKR 18,000
- Comprehensive studies (two or more limbs): PKR 20,000 or higher
Fees can range from gov't vs. private hospital. There may be neurologic testing with some insurance companies; call your company first.
Conclusion
The Electromyography test is a very helpful test that tests muscle function and nerve function. If you acutely get pain, numbness, or weakness in an arm or in a leg, or back pain, this test informs you what is causing it, nerve damage, muscle disease, or neurological disease. If conducted by a specialist, an EMG yields accurate results that translate to successful interventions. Although painful, the benefits of early intervention and diagnosis are worth more than the pain. If your physician requires an EMG test on you, being aware of the reason, preparation, and process will eliminate fear and prepare you well for better outcomes in your healthcare journey.
Book lab tests from the
best-certified labs in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, and get a discount of up to 35%. For assistance, call our helpline at 03171777509 to find the right lab test for your health needs.