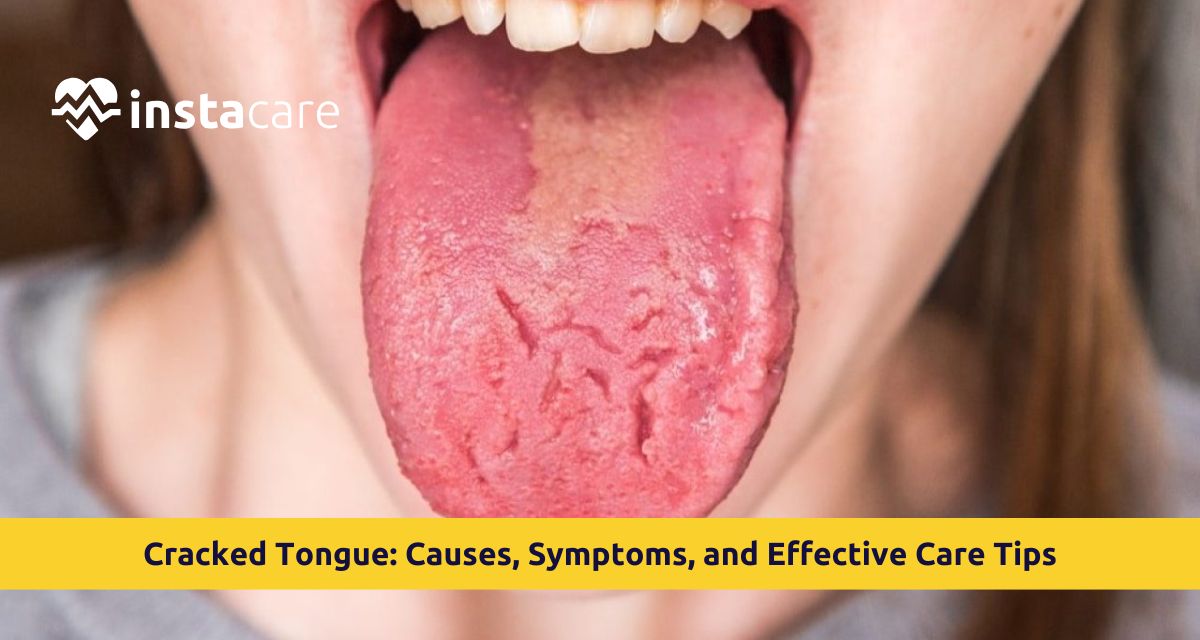
What Is a Cracked Tongue?
Fissured tongue, or lingua plicata, is a benign mucous lesion with numerous grooves, cracks, or fissures across the dorsal surface of the tongue. The fissures are more commonly surface and border in pattern and can be variable in number and depth. Cracks on tongue meaning is never sickness—most of the time, it's birth sickness or developed in a couple of years with no problem. How frustrating the prognosis will be to you, particularly after viewing cracked tongue pictures on the web, most are non-lethal and need little therapy.
Common Causes of a Cracked Tongue
Recognizing causes decides whether or not an individual is to be treated:
- Genetic predisposition: Fissured tongue will be inherited as an acquired benign anatomical variation. Congenital status will be seen in early childhood and with progressive age, the condition will manifest more prominently.
- Vitamin Deficiency: Cracked tongue vitamin deficiency, especially vitamins B (B12, B2, and B3), iron, and zinc may lead to fissures of the tongue.
- Dehydration: Cracked tongue and dehydration are synonymous. Insufficient supply of water leading to drying of the tongue makes existing fissures more apparent.
- Medical Disorders: Fissured tongue has been linked with a number of medical disorders such as cracked tongue and diabetes (since diabetes causes dry mouth), Sjögren's syndrome, psoriasis, and Down syndrome.
- Aging: Tongues fissure with advancing age due to aging.
- Stress and Anxiety: Cracked tongue and stress - Stressed and tense persons may relate fissured tongue with tension and stress as tension and stress are stressing for the tongue due to mouth breathing and grinding of teeth, both of which are tension-causing to the tongue.
- Neglect of Tongue Hygiene: Not cleaning the tongue offers a breeding ground for crevices' bacteria, and cracks are apparent.
Symptoms and When to Be Concerned
While fissured tongue is usually symptom-free, knowledge of cracked tongue symptoms has you checking your mouth:
Common symptoms observed:
- Furrows, cracks, or grooves in the tongue surface
- Wrinkled or ridged tongue appearance
- Gentle soreness with occasional consumption of extremely hot or sour food
- Food particle lodging odor in the sense that particles get lodged in deep grooves
Symptoms Needing a Doctor's Visit:
- Pain, burning, or stinging pain
- Swelling, redness, or white spots
- Symptoms of cracked tongue infection with pus or fever
- Having difficulty eating, swallowing, or speaking
- Bleeding cracking
- Extremely cracked suddenly bursting with other symptoms
If you notice that you have persistent pain, symptoms of infection, or new irritating symptoms, see a health worker or dentist early.
How It's Diagnosed?
A crack in the tongue is most often diagnosed on physical examination. Your physician or dentist will examine your tongue, take the depth and number of cracks and the direction across the tongue that they move, and check your history of symptoms, your diet, and your family history.
If etiology is suspicion of disease or illness underneath, laboratory tests can be performed to exclude inflammatory markers, blood sugar, or nutritional status. Special tests are not usually required for the majority of cases unless by clinical assessment.
Treatment and Care Tips
Cracked tongue treatment is designed for symptom relief and prevention of complications:
- Practice Proper Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day, morning and night, and brush your tongue gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush or a tongue scraper to avoid food particles and bacterial plaque remaining between crevices.
- Stay Properly Hydrated: Drink enough water throughout the day to avoid cracked tongue and dryness. Water within the mouth keeps the tongue soft and healthy.
- Correct Nutritional Deficiencies: Dietary changes or supplements will be administered by your physician if cracked tongue vitamin deficiency is what the physician detects from a test. B vitamins are found in whole grains, eggs, greens, and lean meat.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid extremely hot, sour, or extremely spicy food which will irritate cracks further. Tobacco and alcohol cause cracks as well.
- Use an Antimicrobial Mouthwash: Your dentist may also recommend using an antimicrobial mouthwash at the time of infection in order to discourage bacterial growth.
Cracked tongue home remedies:
- Saline rinse to break up fissures and reduce swelling
- Use sparingly food-grade aloe vera gel in fissures to get rid of inflammation
- Add probiotic foods like yogurt in diet to maintain oral hygiene in balance
- Use a humidifier in dry rooms
Cracked tongue cure naturally: Congenital fissured tongue is "uncurable," yet good oral hygiene, proper fluid intake, and correction of nutritional deficiency will alleviate symptoms and avoid complications.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
Cracked tongue prevention is aimed at oral hygiene management:
- Improve Your Diet: Consume good diet or take supplements, if advised, with proper amounts of B vitamins, iron, zinc, and other materials.
- Daily Oral Hygiene: Brush, floss, and clean tongue once a day to avoid bacterial accumulation that can irritate fissures or infect.
- Six-Monthly Dental Check-Up: See your dentist at six monthly intervals for check-up, professional cleaning, and oral examination.
- Control of Chronic Disease: If diabetes or other chronic diseases, which are linked to cracked tongue, cooperate with your doctor to achieve the best possible control.
- Control Stress: Try stress-controlling therapies such as exercise or meditation since fissured tongue and stress are best friends.
- Stay Hydrated: Water is your beverage, and don't dehydrate with beverages such as alcohol and caffeine.
Although fissured tongue congenital cannot be prevented, they are good habits that make symptoms and occurrence of complications such as cracking infection of the tongue easy.
Conclusion
A cracked or fissured tongue is generally a benign condition and is not treated epidemically. Since you know why the tongue cracks anything from heredity and age to nutritional lack to illness you're able to do something about it. Some of them are so asymptomatic that you'll be completely unaware that you have it, but with good oral health, proper hydration, and fixing the nutritional lack, it won't be a problem. If you have warning signs of pain or infection symptoms of fissured tongue, visit a health worker for further assessment.
Please book an appointment with the
best Dentist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 02137136090 to find a verified doctor for your disease.