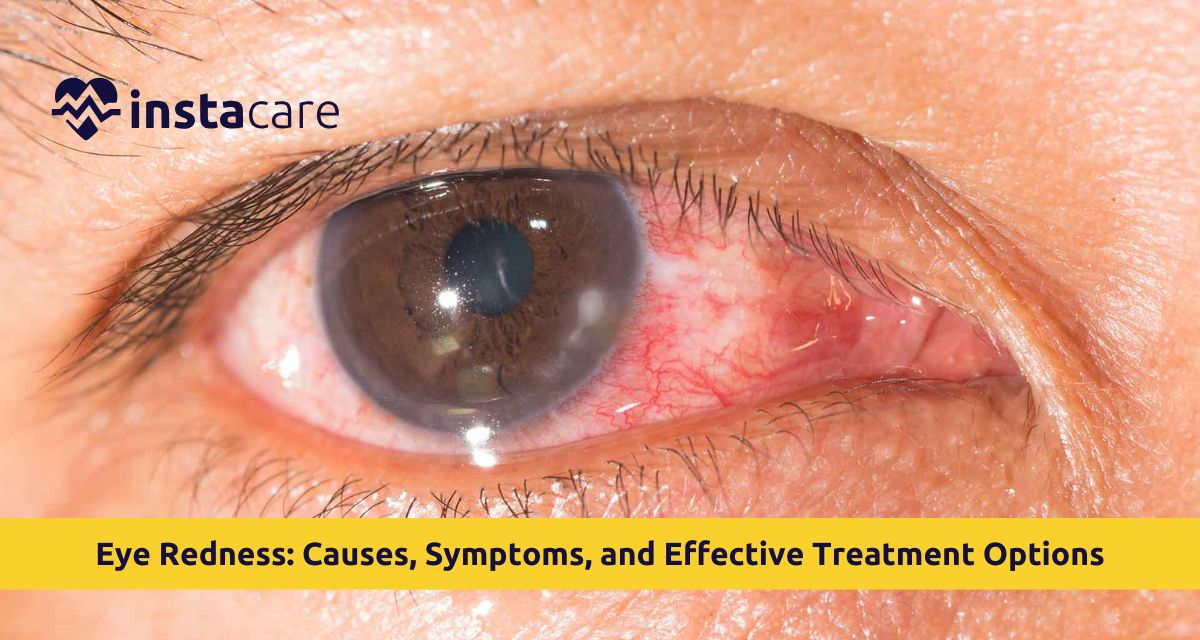
What Is Eye Redness?
Red eyes may be secondary to infection, disease, allergy, habits of life, or environment. Caution is practiced when it is transient, comes and goes in a cyclical manner, or extremely colored. Early treatment prevents complications and a hierarchy of the eye's well-being is created.
Red eyes are caused by engorgement or inflammation of the conjunctival vessels, the thin transparent membrane over the white of the eye. Eyes are reddish-pink. Eyes are most typically related to watering, dryness, irritation, or pain. It must be distinguished from trivial obstructive vision and irritation syndromes. Redness and irritation are permissible, but recurring redness with pain, discharge, or loss of vision are evil signs like infection or
glaucoma.
Common Causes of Eye Redness
It is advisable to understand why the eyes turn red so that it could be prevented and dealt with accordingly. Some of the most common Causes of eye redness are:
- Allergy eye redness – Exaggerated responses to pollen, dust, cat or dog dander, or mold may result in tearing, itching, and redness. Allergy patients will note frequent recurrence.
- Eye redness due to infection – Viral or bacterial conjunctivitis includes redness, swelling, pain, and discharge. Infection is infectious and requires medical diagnosis.
- Dryness, red eyes – Dry eyes are formed when the tears are insufficient or when tears are squeezed out in excessive amounts along with associated redness and swelling. Screen, air conditioning, or chronic exposure to low humidity is most likely to be responsible.
- Red morning eyes – Eyes turn red as a result of episodic dryness, crusted eyes, or overnight contact with an allergen.
- Red eyes after swimming – The eyes turn red by chlorine or other disinfectants added to the pool and which cause irritation to the eyes. The goggles are not used and the eyes are not rinsed. Eye redness after swimming.
- Eye strain – Watching TV or computer screen for two hours, reading, or dazzling shining light results in temporary redness of the eyes.
- Environmental irritants – Wind, dust, pollution, and smoke may redden and inflame the eyes.
- Trauma or foreign bodies – Vasoconstriction due to accidental trauma or foreign bodies.
- Underlying medical conditions – Redness can be due to blood pressure, uveitis, or glaucoma.
Symptoms Associated with Red Eyes
Red eye symptoms differ with etiologic factors. Some of the common symptoms are as follows:
- Red or reddish coloration of eyes
- Poor to quite redness and eye discomfort
- Burning, itch, or stinging isle
- Overlap of tears or watery eyes
- Blurred eyes and vision and redness and vision disturbance in more severe cases
- Light sensitivity of eyes
- Swelling around or of eyelids
- Discharge, crusting, or gluey eyes or Eye redness from infection
Treatment Options
Home remedies for red eyes
The majority of common red eyes could easily be treated by mere red eye home remedies:
- Clean eyes with clear warm water to flush out irritants
- Use cold compresses to decrease redness and swelling
- Use artificial tears to lubricate dryness
- Do not rub your eyes since this will introduce added Eye redness and irritation
- Break screen from time to time to avoid eye strain
- Use hypoallergenic sheets so that allergic reaction is avoided as much as possible
- Drink sufficient water such that one is well hydrated in order to avoid introducing Eye redness and dryness.
Home remedies used above are effective as well as safe excluding the condition caused by self-limiting allergy.
Treatment in Medicine
For chronic or established redness, specialized management by red eye experts will be necessary:
- Allergic conditions - antihistamine or anti-inflammatory drops
- Bacterial or viral infection - antiviral or antibiotic drops
- Chronic conditions such as glaucoma or uveitis - medication
- Lubricating eye drops if the redness and dryness of the eyes are alleviated
- Oral therapy in acute will be advised to control root systemic disease
For relief in emergencies, it is always wise to know how to alleviate red eyes at the same time. Antihistamine drops for eyes, tears, or cold compresses are short-term relief solutions, but persistent reddening needs to be checked by a doctor.
Prevention Tips
Preventing eye redness from having healthy eyes. Healthy practices will discourage redness of eyes:
- Maintain hygiene by washing hands before using the eyes
- Do not exchange make-up, towels, or lenses
- Restrict screen use and follow 20-20-20 rule (refrain from using a screen every 20 minutes)
- Avoid subjecting the eyes to dust, chemicals, or smoke
- Swim in eye goggles to prevent red eyes when swimming
- Use air humidifiers to prevent dryness
- Prevent the allergy through drug and allergen avoidance
- Drink lots to reduce redness and dehydrate eyes
When to Visit an Eye Doctor
Many red eyes are benign, but there are a few situations where one should employ an eye doctor for red eyes:
- Persistent redness lasting more than a few days
- Severe eye redness and pain
- Abrupt change of vision or fuzzy vision (Eye redness and vision problems)
- Discharge, swelling, or crusting
- Wary frequently
- First doctor visit ensures proper treatment, proper diagnosis, and prevents severe complications.
Eye Care Tips
- Do not rub eyes even if they become watery as it will create more inflammation and scratch eyes
- Take out contact lenses whenever there's even a hint of redness to avoid further eye irritation
- Sleep with eyelids tightly closed in order to minimize morning red eyes
- Eat food rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, C, and E for healthy eyes
- Use sunshades to protect eyes from ultraviolet rays when going outdoors during the day
- Using these methods makes it easy to reduce the occurrence of redness of the eyes as well as general ocular comfort.
Conclusion
Red eyes are an infectious but curable disease that arises on account of irritation, allergy, infection, or internal disease. Red eyes treatment and some facts about the red eyes symptoms and the cause of red eyes must be known so that a human can have healthy eyes. Home therapy of transient red eyes, lifestyle modification, and prophylactic care in the form of removal of redness of the eyes by allergens, dryness, or surface irritants can go a long way in the form of ease of eyes.
Please book an appointment with the
Best Eye Specialist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find the verified doctor for your disease.