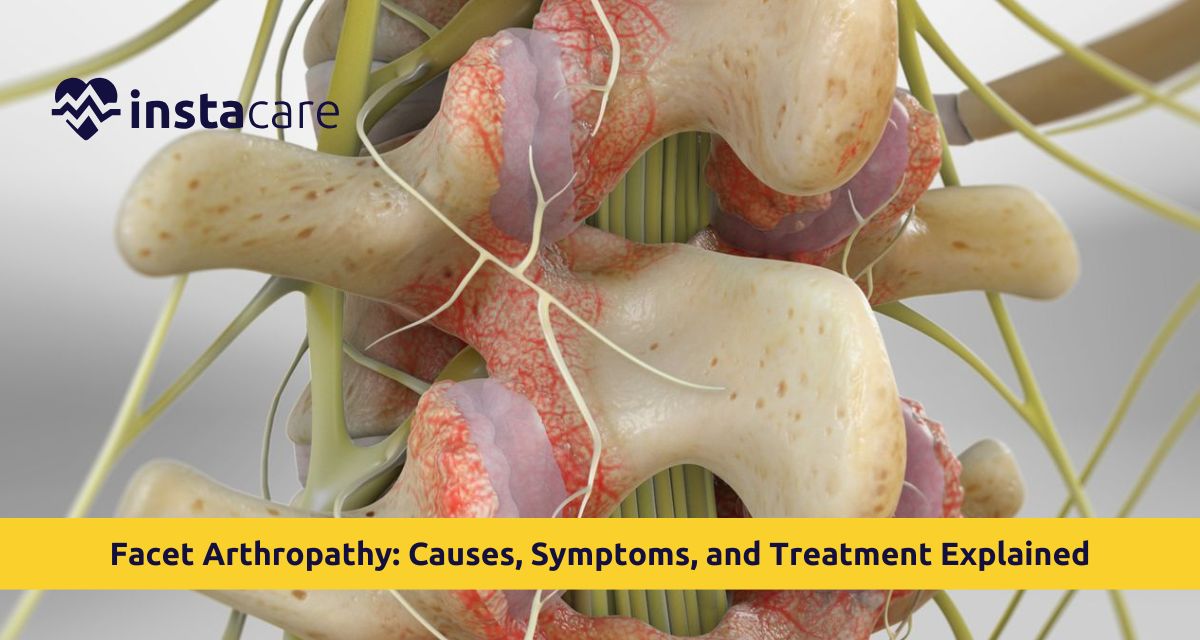
What Is Facet Arthropathy?
Facet arthropathy is degeneration or arthritis in the spine of facet joints. The cartilage is then placed in these joints which are surrounded by a capsule that manufactures fluid to further facilitate movement. With age or injury, such cartilage degenerates causing friction, swelling and pain.
Depending on its location:
- Lumbar facet arthropathy is a back problem in the lower part of the back, and may give the sensation to buttock or thigh.
- Cervical facet arthropathy is a neck disorder, which leads to headaches and stiffness.
The two of them result in the potential of pain in the facet joints, which save mobility but negatively affect life quality.
Causes and Risk Factors of Facet Arthropathy
Facet arthropathy can be a consequence of the wear and tear, yet there is an opportunity that its development can be enhanced by other factors:
- Aging: The natural cartilage and spinal degeneration are the most prevalent ones.
- Repetitive Movements: They are dangerous occupations or tasks that entail repetitive bending, lifting, or twisting.
- Spinal Injury or Trauma: There is the risk that the facet joints are damaged in the accidents or falls.
- Obesity: The overweight causes an added burden on the spine.
- Poor Posture: This is chronic bending, poor body mechanics which leads to strain on the spine.
- Herniated Disc or Spinal Misalignment: these changes the distribution of load on the spine and strain the facet joints.
- Genetic Factors: Spinal arthritis or joint degeneration may be predisposed by a family history.
With time, these aspects result in the degeneration of facet joints, which bring about inflammation, stiffness, and pain that is of a chronic nature.
Common Symptoms of Facet Arthropathy
The facet arthropathy symptoms change with the location and the degree of the disorders. Nevertheless, the common symptoms are:
- Localized Back or Neck Pain: Dull, aching pain that worsens with movement.
- Pain After Rest: This is either stiffness or soreness following prolonged sitting or sleeping.
- Less Range of Motion: Can hardly bend, twist or straighten the back.
- Pain to Limbs Lumbar facet arthropathy can be accompanied by pain that extends to the buttock or thigh, whereas cervical facet arthropathy may be also accompanied by headache or shoulder pain.
- Tenderness: The painful areas are in front of the painful joints.
Facet joint pain, unlike in nerve compression conditions e.g. herniated discs, does not typically result in any numbness or tingling sensation, although this can be used to differentiate between facet arthropathy vs spondylosis.
Diagnosis Facet Arthropathy
The patient exhibits pain in the calf area accompanied by mild fever and no reaction to antibiotics.
The diagnosis of a facet arthropathy starts with the comprehensive examination of your medical history and symptoms. Some of the tests that your doctor can utilize are:
- Physical Examination: Evaluation of the location of pain, movement of the spine, and tenderness of the spine.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays in order to identify a narrowing of the joint spaces or spurs of the bones. CT or MRI to evaluate inflammation of the joints and loss of cartilages.
- Facet Joint Injections: This is a diagnostic injection that is placed in the suspected joint and includes anesthetic medicine and steroid. In case of pain relief, this proves that the source of pain is at the facet joint.
This is very specific diagnosis that can be used to treat facet arthropathy.
Treatment Options for Facet Arthropathy
Facet arthropathy is treated depending on the pain severity and the level of degeneration of the joint. It may include:
Medications
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs (ibuprofen) or acetaminophen, which are available over-the-counter drugs, decrease inflammation.
- Muscle Relaxants: Assist in relieving muscle spasms in the joints of the affected.
- Prescription Drugs: When regular drugs do not treat severe pains.
Physical Therapy
Specialized exercise regime boosts the back and enhances flexibility. Exercises for facet joint pain can involve some light stretching, core strengthening and posture correction.
Facet Joint Injections
The facet joint injections consist of a corticosteroid and a local anesthetic to inflame and temporarily relieve the pain. These injections can also assist in determining the affected joint that is painful.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
When the chronic pain cannot be controlled by the conservative therapies, RFA is aimed at the nerve fibers that send out pain signals through the facet joint and provide long-term pain relief.
Surgical Intervention
In some uncommon instances of severe degeneration of facet joints, surgery of spinal fusion can be applied to stabilize the area affected.
Facet Arthropathy Home remedies and lifestyle
Treatment for facet arthropathy is frequently associated with regular home therapy and changes in lifestyle:
- Keep Great Posture: Do not stoop, sit on ergonomic chairs.
- Keep moving: Walking or swimming are examples of exercises that are not strenuous, yet they increase flexibility.
- Hot/ Cold Treatment: Use ice and hot packs alternately to reduce pain and stiffness.
- Weight Management: healthy weight decreases the spinal pressure.
- Correct Sleep Position: Supportive mattresses and pillows should be taken in order to keep the spine straight.
The habits have the ability to decrease lower back pain from facet arthropathy and inhibit the exacerbation.
Facet Arthropathy Prevention Tips
Although the process of aging cannot be regulated, the following prevention strategies will help to delay arthritis development in the spine:
- Do core-strengthening exercise to help your back.
- Addiction to heavy lifting or twisting should be avoided.
- Have regular rest of long sitting or standing.
- Maintain good spinal positioning in the course of physical activities.
- Take a healthy diet that is rich in calcium, vitamin D and food that fights inflammation.
The early prevention of the degeneration of facet joints can greatly decrease the discomfort in the spine in the long term.
When to See a Doctor for Facet Arthropathy
You need to consult a medical professional in case:
- Home care does not cure pain after over two weeks.
- You are in severe pain of the lower back as a result of facet arthropathy or inability to fully perform due to stiffness of the neck.
- The pain extends to the arms or legs, which suggests the presence of nerve involvement.
- You have the experience of a lack of balance, coordination, or weakness.
Facet arthropathy diagnosis and early assessment will help avoid additional harm to the joint and enhance the results of treatment.
Conclusion
Facet arthropathy is an ordinary, but treatable spinal disorder that develops as a result of degeneration and inflammation of the facet joints. Regardless of the lumbar or cervical affected area, very early diagnosis and treatment with lifestyle change can be very instrumental in enhancing the quality of life. Most of the patients respond to the pain well and recover their mobility with the appropriate mix of medications, physical therapy, and facet joint injections. In case of long-lasting pains in the facet joints, seek the professional attention of your physician to get special care and advice.
Please book an appointment with the
best Physiotherapist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find the verified doctor for your disease.