Diphtheria is a contagious and potentially fatal bacterial infection that affects the throat and, in some cases, other parts of the body. For those who don’t know exactly what it is or how to recognize its symptoms early on, this blog post will provide all of the information you will need to understand diphtheria and how best to protect yourself against it. We'll discuss the causes of diphtheria, its symptoms, risks related to contracting it - particularly people at high risk for developing complications from it - as well as treatment options available if contracted. By increasing your knowledge about this serious disease and understanding preventive measures such as vaccinations and taking precautions where necessary, you can better arm yourself with the means to protect your health.
Diphtheria Outbreak in Pakistan
Diphtheria has become a major public health concern in Pakistan. Estimated to be one of the leading causes of death amongst children under five, it is imperative that both men and women are informed on this illness. Spread by coughing and sneezing it can quickly spread through communities if people are not aware of how to protect themselves against its transmission. In this blog post we will explore what diphtheria is, the signs and symptoms associated with it, as well as precautionary measures to take so you can keep yourself safe during an outbreak. Stay tuned for more information!
What Is Diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a highly contagious bacterial infection that affects the nose, throat and sometimes other parts of the body. It is caused by a microbe called Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which releases toxins into the bloodstream. These toxins can affect various organs, such as the heart and kidneys, making diphtheria dangerous and even fatal in some cases. Luckily, diphtheria can be prevented through immunization with vaccines like DTPa or Tdap. Vaccinating children against diphtheria at an early age is essential for reducing rates of infection in communities across the world - especially since it is more severe when it strikes infants or young children. What's more, boosters are recommended throughout one's life to reduce their risk of contracting this serious illness.
How is it spread and who is at risk?
Diphtheria is an infectious disease caused by bacteria and it can be spread through direct contact with an infected person, or through inhaling the bacteria. It is highly contagious and can spread rapidly within families or in close-knit communities. Furthermore, anyone who has not been immunised against diphtheria is at a high risk of contracting the illness, particularly babies and young children. In order to reduce the spread of diphtheria, it is important that all people are vaccinated, especially those in vulnerable age groups. Persons who have been exposed to someone with diphtheria should also be separated from others as soon as possible and should seek medical attention if they experience any symptoms.
View More: Is Chicken Good for Hemorrhoids
Causes of Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection which can be serious and life-threatening, caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheriae. It is spread through respiratory secretions (such as sneezing and coughing) or contact with objects that have been contaminated with these secretions. While it can affect people of any age, young children are especially vulnerable to this contagious disease. Vaccines for diphtheria are available, making it an easily preventable condition if immunization schedules are adhered to in accordance with public health recommendations from local health departments. To reduce the chance of getting infected, it's important to keep up to date on vaccinations and practice good hygiene such as washing hands frequently.
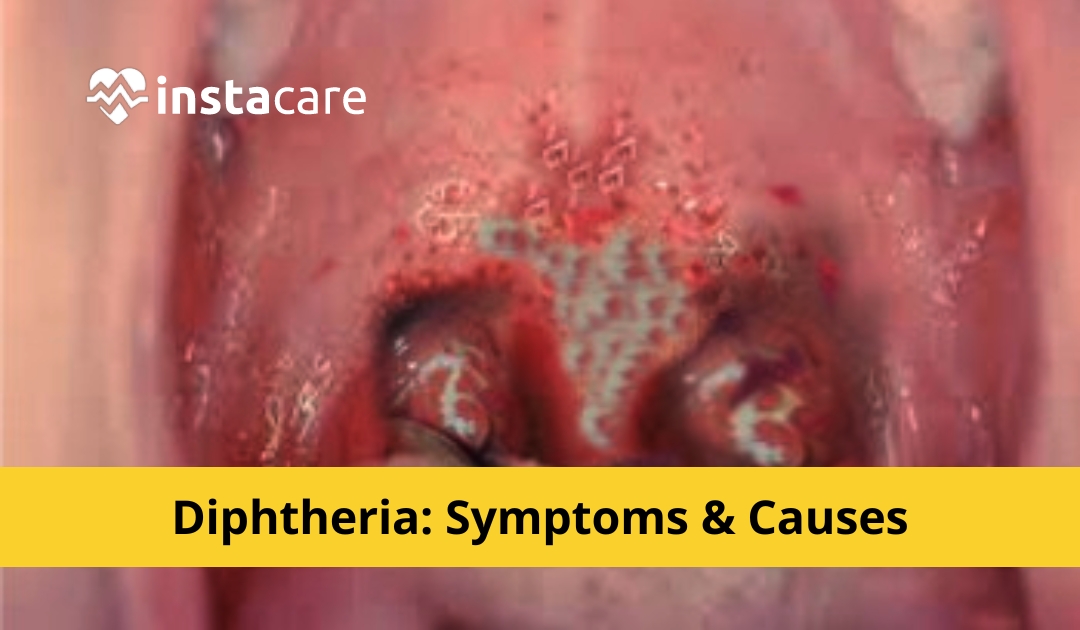
Diphtheria Symptoms
Diphtheria is an infectious bacterial disease that can be life-threatening unless the person gets the right treatment. Common early symptoms include a mild fever, sore throat, and swollen glands in the neck. As the infection progresses, a gray or white coating may form over the back of the throat and tonsils. This coating is called a pseudo membrane, and it is composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria and other substances. Coughing, breathing trouble and heart problems are other signs of diphtheria. In rare cases, complications such as nerve damage or paralysis may occur if medical treatment is not given quickly enough. It's important to seek medical help as soon as any suspicion of this condition arises to avoid such serious consequences.
Complications of Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a serious and potentially fatal infectious disease caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. While the disease can be prevented through immunization, an estimated 10-20% of those infected experience complications that can range from mild to severe depending on their age and overall health. Such complications may include damage of the heart and nervous system, leading to breathing problems, paralysis of certain muscles, or even loss of hearing. In some cases, if left untreated, diphtheria may cause death. Early diagnosis and supportive care are necessary in order to prevent serious complications associated with this highly contagious illness.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of diphtheria begins with a physical examination and medical history. During the physical exam, a healthcare practitioner will look for signs and symptoms associated with the infection such as fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, weakness and fatigue. Based on this assessment, additional tests may be recommended such as laboratory tests to detect bacteria in the blood, urine or secretions of the nose and throat. A cotton swab can also be taken from these areas which is then tested using special laboratory techniques to detect the bacteria present. Imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans may also be used to check if there are any complications caused by diphtheria such as an enlarged heart or lung disease. Prompt diagnosis can help ensure early treatment of this serious infection.
Diphtheria Treatment
Diphtheria is a serious infectious disease caused by the bacteria Corynebacterium diphtheriae, and can lead to complications such as heart failure and nerve damage. Treatment for diphtheria involves antibiotics, along with supportive treatment in the form of fluids and nutrition. There may also be treatments necessary should any complications arise, such as breathing or cardiac support. Vaccines are available which work to protect against the development of this unpleasant condition. Although these vaccines have been around since the 1920s and are widely used in many countries, diphtheria is still found among people who aren't vaccinated - it is therefore important to ensure you're up to date with your immunizations. Seeing a health professional if you feel ill or suspect that you or someone you know is infected with diphtheria is vital - early diagnosis ensures better outcomes.
Home Remedies
Diphtheria is a bacterial upper respiratory tract infection that can be serious if not treated properly. Fortunately, there are many home remedies that can be used to alleviate the symptoms of diphtheria, such as garlic, licorice root, turmeric and apple cider vinegar. Garlic has antibiotic and antiviral properties and can help boost the immune system. Licorice root can help reduce sore throat pain, as well as coughing. Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory that can also reduce pain and swelling. Finally, apple cider vinegar is effective for reducing fever and relieving tiredness or fatigue associated with diphtheria. When used consistently and correctly, these natural treatments combined with conventional pharmaceuticals may greatly improve outcomes for sufferers of the illness.
Prevention of Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infection that can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. Luckily, there are steps every individual can take to help prevent the spread of this disease. Vaccination is one of the most effective preventive measures against diphtheria, and certain countries have a high rate of immunization which has helped contain its spread. Additionally, simple hygiene and sanitation practices like regularly washing hands and not sharing items such as utensils or towels with ill individuals are important in preventing the transmission of germs like those responsible for diphtheria. Lastly, infections can be effectively treated with antibiotics during their early stages so immediate medical attention should be sought if symptoms present themselves in order to stop its progression before it’s too late.
Vaccination against Diphtheria
Vaccinations against diphtheria are one of the best preventative measures a person can take to stay healthy. Vaccinating helps protect an individual, but it also protects those who cannot be vaccinated due to age or other medical conditions. Types of these vaccines will vary upon location, and a healthcare professional should be consulted in order to determine which is right for you. The most common form is an injection given at least two times in a lifetime and may need repeating if the individual travels abroad or their immunity levels weaken over time. Vaccination against diphtheria is recommended and is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of contracting this dangerous disease.
View More: 10 Worst Foods for Diarrhea - What to Eat In Diarrhea
Resources on Diphtheria
Resources on diphtheria are essential, as it helps to diagnose, prevent, and treat the disease, one of the deadliest bacterial infections in history. A key resource is a qualified medical professional who can help diagnose the condition and guide appropriate treatment. In addition, organizations such as the World Health Organization provide accurate facts and research-based information about diphtheria to educate individuals on prevention. Health officials such as doctors also have resources that can assist with a patient's recovery. For example, medicated mouthwashes may be prescribed to reduce symptoms associated with the harmful bacteria that cause diphtheria. Finally, there are online self-care resources that can provide guidance and support for those struggling with the illness. Overall, having access to the right resources can mean the difference between life and death in relation to this serious disease.
Are there any complications associated with Diphtheria?
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infection caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae bacteria, which typically takes hold in the throat and nasal passageways. Its symptoms usually include a sore throat, swollen glands in the neck, fever, and weakness. While vaccines exist to help prevent diphtheria infections, complications can still arise after developing the infection. Common complications of diphtheria include pneumonia, shallow breathing, delirium due to high fever, as well as damage to organs like heart valves and other tissues that can lead to heart failure or severe respiratory problems. If treated early with antibiotics these complications can be avoided; however, left untreated can sometimes lead to lasting neurological issues including paralysis and death. Therefore it is important to get treated as soon as possible if you suspect you might have contracted diphtheria to avoid any longer-term repercussions.
Diphtheria Meaning in Urdu
Diphtheria is a serious infectious disease with possible life-threatening complications. In Urdu, it is known as ????'. The disease is caused by bacterium ‘Corynebacterium diphtheria and spreads from person to person through close contact. A characteristic symptom of this contagious condition is the formation of the thick layer at the back of the throat and on the tonsils, which can make breathing difficult. Furthermore, diphtheria may affect other organs like eyes, skin, heart and brain if left untreated. Thankfully, there are highly effective vaccines available today; however, vaccination against diphtheria is still important since the bacteria causing this life-threatening condition can become resistant to antibiotics over time.
Conclusion
Diphtheria is a serious bacterial infection that primarily affects the nose and throat. It can cause severe respiratory problems, paralysis, and even death. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for the best possible outcome. If you or your child develop any of the symptoms associated with diphtheria, see a doctor immediately. With early diagnosis and treatment, diphtheria is usually not life-threatening.
Please book an appointment with the Best ENT Specialist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03100002273 to find the verified doctor for your disease.
Source: https://instacare.pk/blog/diphtheria-symptoms-causes-treatment