Mycoses, which are also referred to as fungus, are infections of the body or part of the body that are caused by the overgrowth of fungi. As much as fungi are natural constituents of the environment and the microbiome of the body, imbalance or compromised immune system may result in infections. These infections may touch the skin, nails, the mouth, or even internal organs, causing mild discomfort and up to serious health complications. The general health condition is important in understanding the Fungal infection treatment and Fungal infection prevention.
What Are the Causes of Fungal Infections?
Fungi are likely to proliferate in warm and damp conditions and therefore some body parts are more prone. Common causes include:
- Weakened immune system
- Long-term antibiotic/corticosteroids.
- Uncontrolled sweating of the body or wet garments.
- Poor hygiene
- Long term illnesses like diabetes.
Some fungi, such as Candida are harmless but they cause yeast infection when they are overgrown. There are other, like dermatophytes, which cause skin fungal infection as well as ringworm infection.
Types of Fungal Infections (Mycoses)
Fungal diseases are categorized according to the body region they attack:
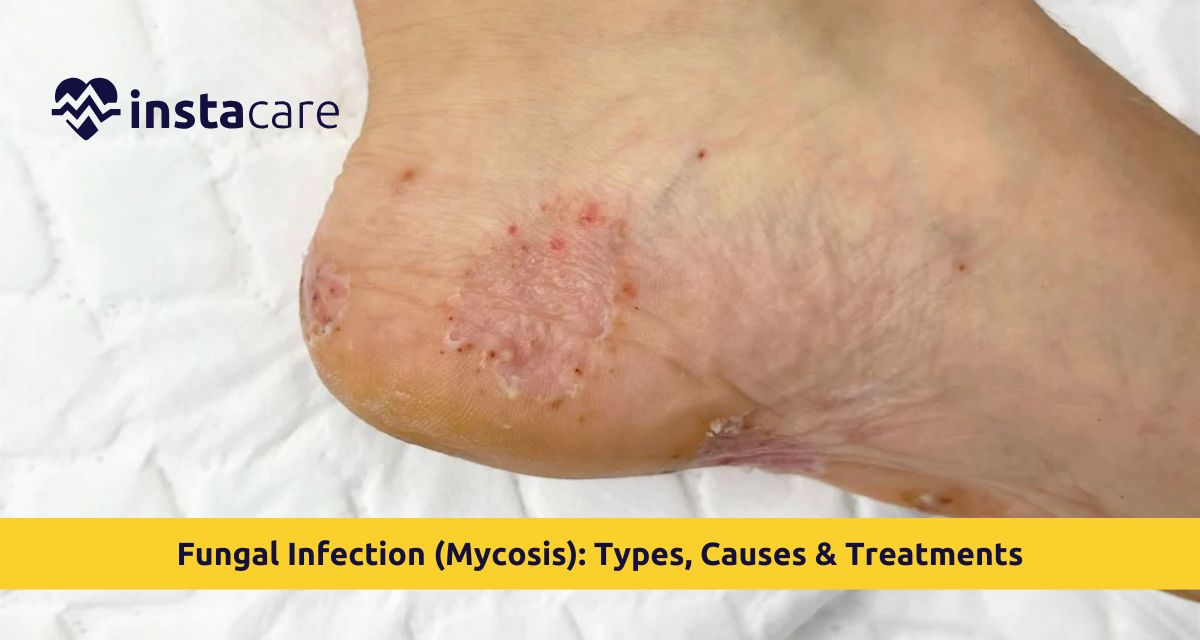
- Superficial Mycoses: This is affecting the skin, hair and nails. They include fungal infection of the nail, Athlete’s foot fungal infection and fungal infection of the ringworm.
- Subcutaneous Mycoses: This occurs on deeper skin layers and connective tissue and is normally caused by fungi penetration through the cuts.
- Systemic Mycoses: Affect internal organs including the lungs or the brain and in most cases in those with compromised immune systems.
- Opportunistic Mycoses: These infections are as a result of the normally harmless fungi that become pathogenic in individuals with weakened immunity. A typical example is Candada infection.
Common Symptoms of Fungal Infections
The symptoms are different, based on the nature and location of the infection, yet some of the most common ones are:
- Scaly, erythematous, or itchy, skin patches.
- Split nails (fungal nail infection) or discolored nail.
- Oral yeast infection (white spots in the mouth or the throat).
- Several urinary tract infections include burning or discomfort during urination (urinary yeast infection).
- The recurring fatigue of system fungi.
The early awareness of these symptoms may help make fungal infections diagnoses and treatment faster.
Read More: Are Sinus Infections Contagious?
Diagnosis of Fungal Infections
Fungal infection diagnosis normally consists of a combination of:
- Physical inspection of the affected regions.
- Skin, nail or hair sample microscopic analysis.
- Examination of culture to determine the type of fungus.
- Systemic infection Blood tests or imaging.
The right antifungal medication can only be prescribed with the right diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Fungal Infections
The therapy program will be based on the type and the severity of the infection:
- Topical Antifungal Medications: Creams, ointments or lotions that are applied to the area of infection directly onto the skin in the case of fungal infection of the skin or fungal infection of the athlete feet.
- Oral Antifungal Drugs: Are used to treat fungal nail infection, chronic fungal infections or systemic mycoses.
- Home Care: Cleaning and drying up of the affected areas, wearing breathable clothes, and sharing personal items should be avoided.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Control of blood sugar, boosting immunity and good hygiene.
The entire treatment process should be adhered to in order to avoid relapse.
Prevention of Fungal Infections
To minimize the chances of having a fungal infection, the following preventive measures can be used:
- Wash hands and take shower after perspiration.
- Wear dry pair of breathable socks and shoes.
- Do not share such personal things as towels or nail clippers.
- Keep skin folds clean and dry
- Clean communal areas regularly.
Prevention of fungus infection is of particular concern to individuals that have chronic illnesses or low immune system.
When to See a Doctor?
See the doctor when you are experiencing:
- Constant or progressive fungal infection of the skin.
- Discolored, thickened, and painful nails.
- Recurrent yeast infection
- Fever, malaise, or systemic infection.
- Poor outcomes of over-the-counter medication.
Early consultation means that there is proper management and minimization of complications.
Conclusion
Fungus is widely spread and can be easily treated with the proper use of hygiene, prompt diagnosis, and the employment of antifungal drugs. Be it an infection of the fungus of the ringworm, or athlete foot, or fungus in old age, it is important to know the causes, symptoms, and treatment options so as to prevent the recurrence. Preventive measures and keeping things clean and dry can help to a great extent.