What is a Suprapubic Catheter?
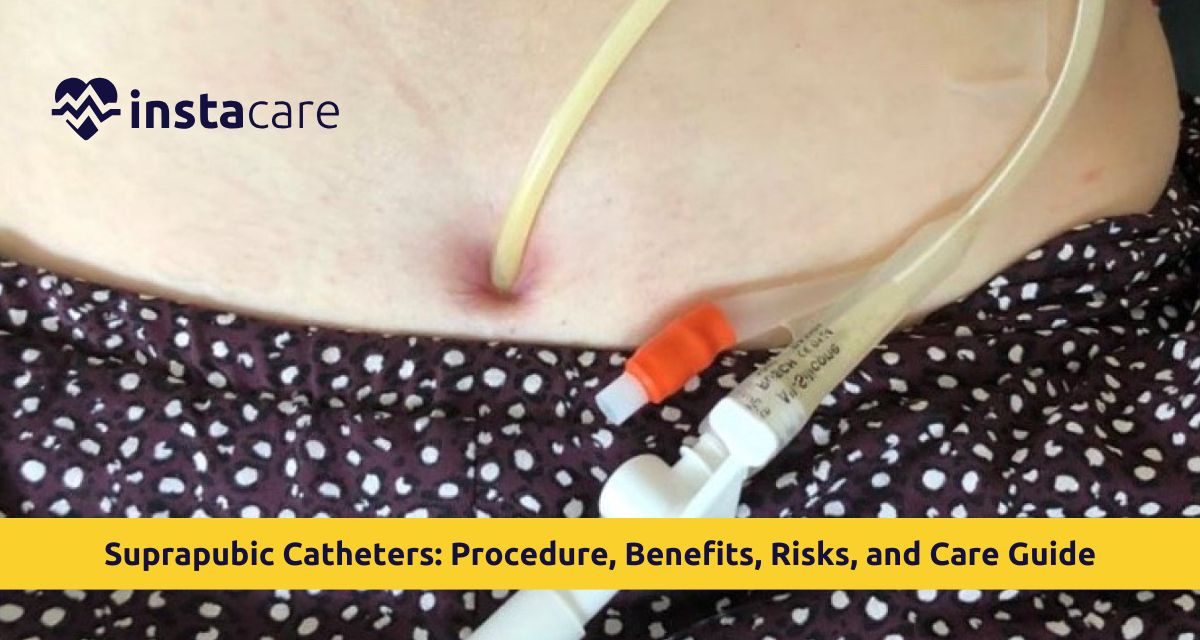
A suprapubic catheter is a soft tube inserted directly into the bladder by making small cuts into the bottom of the lower abdomen, above the pubic bone. Unlike urethral catheters inserted via the urethra, this catheter allows for a bypass route for the drainage of urine. The tube is attached to a leg-worn or bed-held drainage bag, draining continuously with urine.
Suprapubic catheter vs Foley catheter contrast reveals extreme differences. Foley catheters are placed by way of the urethra, while suprapubic catheters go around the natural pathway altogether. Suprapubic catheters are most effective on patients requiring chronic bladder drainage because they avoid urethral trauma and its associated complications. The instrument is typically a soft, pliable rubber or silicone plastic catheter supported by an inflatable balloon inside the bladder, similar to urethral catheters.
Indications for Suprapubic Catheterization
Suprapubic catheter indications span a variety of medical conditions in bladder function:
Urinary Retention Problems:
- Chronic urinary retention with intervals of neurological disease
- Prostatic obstruction to normal voiding
- Bladder muscle dysfunction
- Failure of conservative care
Urethral Pathology:
- Urethral trauma or stricture
- Pelvic trauma that compromises urethral integrity
- Chronic urethral catheter-associated urinary tract infection
- Failed or painful urethral catheterization
Neurological Disorders:
- Spinal cord injury
- Multiple sclerosis
- Other neurological diseases for chronic drainage
Surgical Indications:
- Complex pelvic surgery
- Bladder reconstructive surgery
- Situation in which urethral access cannot be used
- Cases of prolonged catheterization following surgery
The Procedure
Suprapubic catheter insertion is usually performed within a procedure suite or operating room of a hospital under general or local anesthesia. Procedure takes around 30 to 45 minutes.
Pre-Procedure Steps:
- Inflation of bladder for visualization and exposure
- Abdomen antiseptic solution wash
- Administration of corresponding anesthesia
- Ultrasound or cystoscopy guidance preparation
Insertion Process:
- Two to three widths above pubic bone, small incision
- Gradual penetration through abdominal wall into dome of bladder
- Insertion of guidewire catheter or trocar
- Internal balloon with sterile water to be tight
- External part attached with drainage system
- Sterile dressing on site of insertion
Recovery Schedule:
Suprapubic catheter procedure recovery includes mild bladder cramping and discomfort for a few days. Blood-tinged urine normally normal. Return to normal activities within 1-2 weeks. Full healing of the tract in several weeks.
Benefits of a Suprapubic Catheter
Suprapubic catheter benefits are to distribute across physical comfort, infection prevention, and quality of life improvement:
Physical Comfort:
- Saves urethra from erosion and trauma
- Prevents long-term urethral strictures due to catheterization
- Decreases discomfort upon activities of daily living
- Makes sexual intercourse easier without urethral obstruction
Fewer Infections:
- Fewer than urethral catheters
- Convenience in maintenance of cleanliness of abdominal site
- Less likelihood of bacterial colonization
- Improved suprapubic catheter infection prevention outcomes
Quality of Life:
- Enhanced dignity and self-esteem
- Easy to conceal under clothes
- No genital management required for care
- More independence with day-to-day management
Practical Benefits:
- Painless and simple catheter changes once tract formed
- No anesthetic required for day-to-day exchange
- More mobility and ease of movement
- More capacity for exercise and travel
- Sufficient for long-term suprapubic catheter use
Read More: Urine C/E (Complete Examination) Test – Purpose, Procedure & Results
Risks and Complications
Even though there are numerous benefits, suprapubic catheter complications have to be vigilantly observed:
Incidence of Complications:
- Infections: UTI or skin infection where catheter is inserted
- Catheter blockade: Sediment, clots, or encrustation
- Bladder spasms: Involuntary bladder contraction with cramping and leakage
- Dislodgment of the catheter: Tract closure risk if catheter is expelled
Warning Signs of Infection:
- Temp > 100.4°F
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Increased bladder spasms
- Redness or drainage around catheter site
- Pain or swelling over the insertion site
Severe Suprapubic Catheter Risks:
Suprapubic catheter risks include bleeding during or following catheter insertion, trauma to bowel during procedure (rare), irritation of skin at site of stoma, and early displacement with urgent replacement.
Long-Term Complications:
- Delayed formation of catheter encrustation over time
- Stone formation in bladder
- Change in bladder wall structure
- Chronic inflammation to be anticipated
Daily Care and Maintenance
Suprapubic catheter care on a daily basis prevent complications and enable optimal function:
Daily Hygiene Routine:
- Clean around insertion site with soap and water
- Dry skin surface carefully (no rubbing)
- Replace with new dressing if needed
- Rough chemicals or harsh scrubbing to be avoided
- Evaluate site once daily for infection
Catheter Management:
- Instill drainage system below bladder level
- Keep tubing kink-free
- Secure catheter to avoid pulling or tension
- Drainage bags two-thirds full when emptied
- Use leg bag for daytime, bedside bag for nighttime
Fluid Intake Guidelines:
- Have 8 glasses of water a day (unless contraindicated)
- Drink to flush the system
- Check urine color, clarity, odor
- Avoid excessive use of caffeine or alcohol
When to Call for Medical Help:
- Over 100.4°F fever
- Heavy bleeding or excess pain
- Broken or dislodged catheter
- Unable to urinate
- Infection at insertion site
- Recurrent bladder spasm
Routine Care:
- Catheter change every 4-12 weeks
- Daily follow-up visits
- Tract integrity tested professionally
- Drainage bag change as needed
Living with a Suprapubic Catheter
Suprapubic catheter management at home adjustment is linked with accommodation at a functional and emotional level. Clothing selection that accommodates drainage bags and catheter siting normalizes appearance. Day leg bags promote mobility and discretion with larger bedside bags that are secured at night to prevent sleep disruption.
Physical activity generally goes on with adequate precautions. Suprapubic catheter for urinary retention patients can exercise, swim (with waterproof precautions), and resume normal activity. Contact sport or activity related to catheter trauma is avoided. Sexual intercourse also is not excluded and generally better than intercourse with urethral catheterization.
Preparation for the trip includes carrying adequate supplies, including backup catheters, drainage bags, and sterilization solutions. Catheters and other medical equipment are given special attention by airlines, and advance preparation makes travel easy. Adhering to regular care during travel prevents complications.
Psychological adjustment through patient groups, counseling, or the internet assists people in becoming accustomed to it. Most patients have initial fear, which decreases after they are skilled in care techniques and become independent again.
Conclusion
Suprapubic catheters provide efficient long-term drainage of the bladder in such patients who are unable to void spontaneously or require an alternative to urethral catheterization. While acclimation and insertion take time, the benefits of the suprapubic catheter—fewer urethral complications, increased comfort, and improved quality of life—make this a viable option very much deserving of discussion in appropriate candidates.
Suprapubic catheterization can be successful with proper insertion technique, gentle daily care, and prompt detection of complications. With adequate knowledge regarding suprapubic catheter care, management, and prevention of infection, patients can maintain active productive lives with successful fulfillment of their urinary drainage needs.
Please book an appointment with the
best Urologist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and all major cities of Pakistan through
InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your disease.