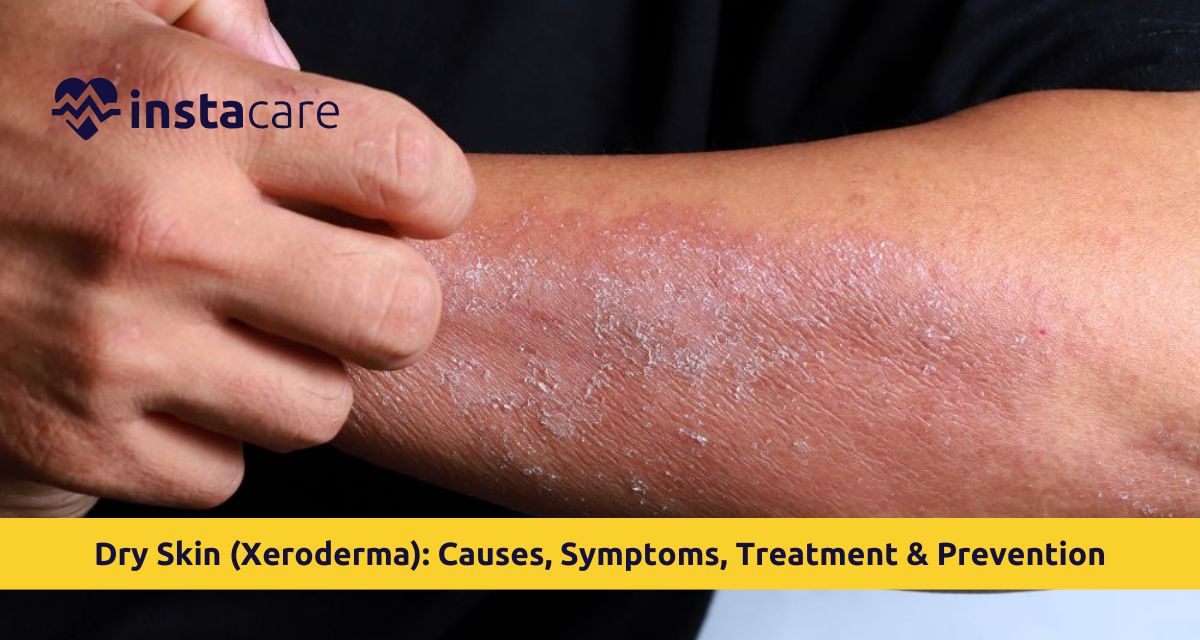
Dry skin, or Xeroderma, is a common condition that occurs when the skin loses excess moisture or oil. Severe dry skin is usually painful but may also cause itching, cracking, and infection if neglected. Dry skin can be a result of environmental factors, lifestyle habits, underlying health conditions, and other factors. Learning about the reasons of dry skin and the correct approaches to the care will allow to regain the condition of the skin and avoid the cases of its reappearance.
What Is Xeroderma?
Xeroderma is abnormally dry skin that lacks sufficient moisture and natural oils. Healthy skin is hydrated by a protective barrier composed of lipids and natural moisturizing factors. Once this barrier becomes weak then the moisture is lost causing a lack of moisture, irritation and rough texture.
Dry skin may be a transitory or chronic condition which may occur among individuals of any age. There are instances in which extreme skin dryness can indicate a medical condition that requires medical attention.
What Causes Dry Skin (Xeroderma)?
There are several internal and external causes of dry skin that cause the lack of water in the skin. Common causes include:
- Cold weather or dry weather, and dry skin in winter.
- Overbathing with hot water.
- Severe dermatological items, skincare products, or detergents.
- Aging that decreases natural oil production.
- Low-humidity environments
- Dehydration
- Certain medications
- Eczema or psoriasis of the skin.
The key to selecting effective options of dry skin treatment is to identify the root cause.
Common Symptoms of Dry Skin
Symptoms of dry skin may be mild irritation to severe irritation. Common Xeroderma symptoms are:
- Rough, flaky, or scaly skin
- Tight or stretched feeling
- Scally dry skin, particularly after bathing.
- Redness or inflammation
- Fine cracks or fissures
- Peeling or shedding skin
These symptoms can worsen and lead to pain or secondary infections if left untreated.
Areas Commonly Affected by Dry Skin
Dry skin may occur at any place but some places are more likely than others because of the few oil glands or exposure.
Commonly affected areas:
- Hands and fingers
- Arms and legs
- Feet and heels
- Face, in particular, cheeks and lips.
- Elbows and knees
Specific skin oils and salves can be used to protect such sensitive areas.
Risk Factors for Xeroderma
Some individuals are at higher risk of developing dry skin due to personal or environmental factors. Higher risk groups include:
- Older adults
- Individuals in cold or dry climates.
- People who habitually wash their hands regularly.
- Chronic skin condition patients.
- Individuals with diabetes or thyroid diseases.
Knowledge of these risk factors is useful in the prevention and management of these risks at early stages.
How Dry Skin Is Diagnosed?
In most cases, the diagnosis of dry skin is based on physical examination and medical history. A dermatologist can evaluate the appearance, texture, and distribution of dryness of the skin. Additional assessment might be necessary in case:
- Drought is harsh or chronic.
- There is bleeding of cracks or infection.
- The other symptoms indicate a pre-existing condition.
Severe cases of dry skin respond better to early diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Dry Skin
Treatment is aimed at replacing the skin barrier and moisture. Treatment involves:
- Extreme dryness ointments.
- Inflammatory prescription creams.
- Intense itching Antihistamines.
- Solving underlying medical conditions.
Flare-ups are minimized by consistent application of prescribed dry skin treatment products.
Home Care & Daily Skin Care Tips
Daily habits are instrumental in managing Xeroderma and preventing its recurrence. Practical home care tips:
- Apply no perfume cleansers.
- Take a bath in warm water rather than hot.
- Apply moisturizer after taking a bath.
- Use creams rather than lotions to improve hydration.
- Wear light breathable clothes.
- In dry conditions, use a humidifier.
- Keep yourself hydrated during the day.
These dry skin remedies are used to reinforce the natural skin moisture barrier.
Prevention of Dry Skin
The treatment of severe symptoms is difficult, which is why it is easier to prevent Xeroderma. Some preventative steps
are:
- Warming up against cold winds.
- Using sunscreen daily
- Avoiding over-exfoliation
- The use of soft skincare products.
- Eating a healthy diet that is balanced in fats.
Itchy dry skin and long-term damage is a major effect of proactive care which is minimized.
Conclusion
Xeroderma (dry skin) is a common disorder that can lead to discomfort, poor skin quality, and impaired appearance when neglected. A majority of the cases can be addressed by understanding its causes, identifying its symptoms at the early stages, and adhering to the appropriate skincare practices. It does not matter whether the seasonal or chronic dryness occurs, regular treatment and proper care will restore the hydration and ensure that the skin stays healthy throughout a year.
Please book an appointment with the Best Dermatologist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and other major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your condition.