Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a strong androgen hormone that
has important roles in the growth of humans particularly in males. Although
some aspects of the body cannot sustain without it, an imbalance in the amount
of DHT is very closely associated with hair loss, prostate, and hormonal
problems. Understanding the hormone DHT, its mechanism of action, and its effects on the human body would enable individuals to make better decisions regarding hair health and hormonal balance.
This blog examines DHT and hair loss, its presence in both men and women, signs of elevated or decreased levels of DHT, available tests, and possible treatments of the disease including DHT blockers and DHT inhibitors.
What Is Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)?
Dihydrotestosterone is a testosterone derivative. It is developed when the enzyme 5-alpha reductase is used to transform testosterone into DHT in the body parts like the skin, scalp, prostate and liver. Dihydrotestosterone function activity contains:
- Male reproductive organs development.
- Control of hair on the face and the body.
- Libido and sexual functional contribution.
- Ingestion effect on prostate growth.
Though DHT is stronger compared to testosterone, it exists in fewer concentrations in blood.
DHT and Testosterone Correlation
The relationship between DHT and testosterone is crucial to hormonal balance. Testosterone is the precursor hormone, and DHT proves to be more active in some tissues. Key points:
- It is only a fraction of testosterone that transforms to DHT.
- DHT binds more strongly to androgen receptors.
- Being overconverted can reduce testosterone.
- Inhibition of DHT does not kill testosterone production.
This balance is essential, as the two hormones have discrete and interacting functions.
DHT Levels: What's Normal?
Depending on age, sex, and overall health, DHT levels vary. The normal concentration of DHT in men is higher than that in women, although both require some concentration to perform their normal functions.
- Adult men: Moderate to high physiological range.
- Women of adult age: Much lower levels.
- Elderly people: DHT can decrease or lose its balance.
Genetics, drugs or illnesses may cause the hormonal imbalances.
DHT in Men
Men with DHT are essential in puberty which helps to:
- Deepening of the voice
- Facial and body hair growth
- Male development of the genitals.
- Nevertheless, the overabundance of DHT in adulthood is linked with:
- Male pattern baldness
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Acne and oily skin
Healthy levels of DHT are also beneficial in the long-term hormonal health.
DHT in Women
Although present at lower concentrations, DHT in women still contributes to hormonal balance. The possible consequences of high levels of DHT in women are:
- Androgenic alopecia or hair thinning.
- Hirsutism (excessive growth of facial hair).
- Acne and oily skin
- Menstrual irregularities
Women who have such conditions as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) tend to be more sensitive to DHT.
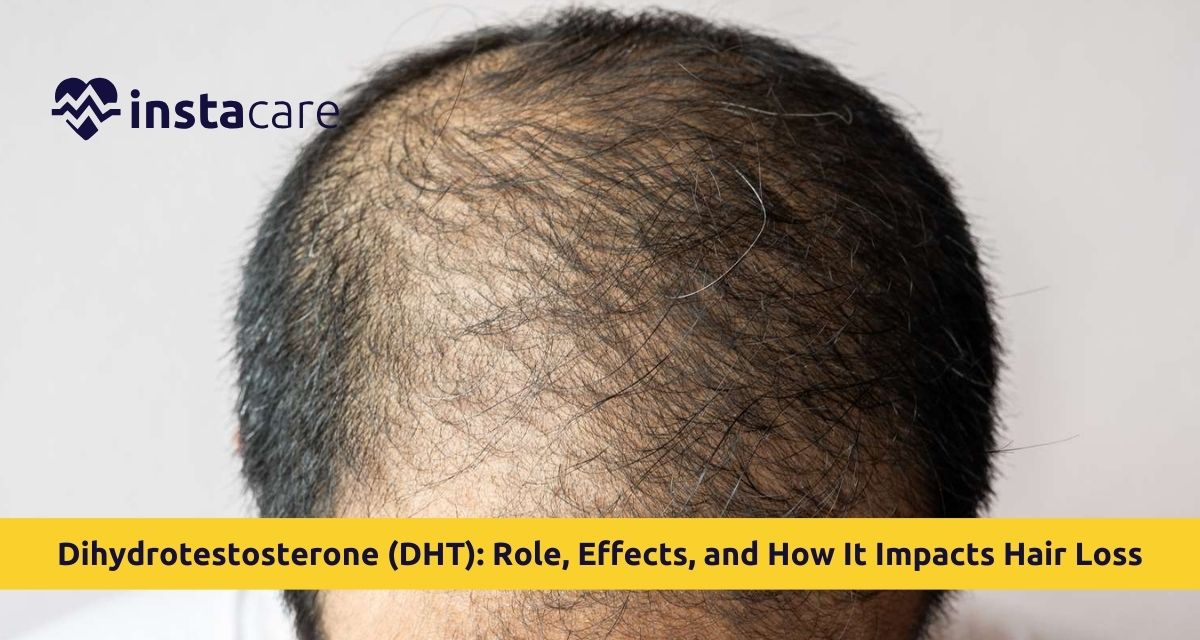
DHT and Hair Loss
The relationship between DHT and hair loss is well-known. DHT interacts with androgen receptors in hair follicles (especially those in the scalp), leading to follicular miniaturization. How DHT causes hair loss:
- Reduces the duration of the hair growth cycle.
- Dilates hair follicles with age.
- Grows finer weaker hair.
- Finally causes hair to cease growing.
The process is referred to as DHT-induced androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness.
High DHT Symptoms
Excessive production of DHT or sensitivity to DHT may result in apparent physical changes. The typical high DHT symptoms are:
- Hairline recession or loss of hair on top of the head.
- Growth of body / facial hair.
- Skin: Oily and with acne.
- Men prostate enlargement symptoms.
- Mood swings (aggression, irritation)
These symptoms can accumulate and worsen over time without treatment.
Low DHT Symptoms
Although high levels are of greater concern, low DHT symptoms may influence health. Possible symptoms include:
- Reduced libido
- Fatigue or low energy
- Decreased muscle mass
- Mood changes or depression
- Sexual retardation (in younger men)
Low DHT may be caused by excessive consumption of DHT
inhibitors or hormonal disorders.
DHT and Prostate Health
DHT and prostate health are closely linked. DHT promotes the growth of prostate cells, which are required during development, but can cause problems in later years.
- High levels of DHT have potentials of leading to enlargement of the prostate.
- BPH is frequently treated by reducing DHT levels.
- Reduction in DHT can alleviate urinary symptoms.
Nevertheless, long-term suppression is to be supervised within the medical care.
DHT Test: How It's Measured
DHT test is a test that determines the concentration of dihydrotestosterone in the blood and is normally ordered when there is a suspected hormonal imbalance. Testing could be suggested in case of:
- Unexplained hair loss
- Prostate concerns
- Hormonal disorders
- Signs of androgen surplus or shortage.
It should always be accompanied by testosterone and other hormone results.
DHT Blockers and DHT Inhibitors
The DHT blockers and DHT inhibitors act by decreasing the conversion of testosterone into DHT. Common options include:
- Prescription drugs (e.g., 5-alpha reductase inhibitors)
- Plant-based extract natural supplements.
- Scalp topical therapy.
These form of treatment are popular in the treatment of prostate and hair loss.
DHT Supplements: Absolutely or Not?
DHT supplements are uncommon and are marketed to individuals seeking to increase their hormone levels. Nevertheless, artificial augmentation of DHT may increase the risk of prostate complications and loss of hair. Supplement use should be:
- Carefully evaluated
- Following the results of hormone tests.
- Sanctioned by a healthcare provider.
Long-term harm from the supplementation can happen unsupervised.
Managing DHT Naturally
Hormone balance can be changed by lifestyle. Helpful strategies include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Reducing chronic stress
- Getting adequate sleep
- Not taking too much anabolic supplements.
- Consult the doctor before using hormone-altering products.
These strategies are able to maintain healthy levels of DHT without violent intervention.
Conclusion
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a crucial hormone in the development of humans and hormonal control, although its disproportion may cause serious health issues. DHT and hair loss to DHT and prostate health, it is important to know the role that this hormone plays in order to control its impact.
People can protect their hair, hormonal health, and well-being by monitoring DHT levels, identifying symptoms at an early stage, and applying appropriate treatments, including DHT blockers, responsibly.
Please book an appointment with the Best Dermatologist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and other major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your condition.