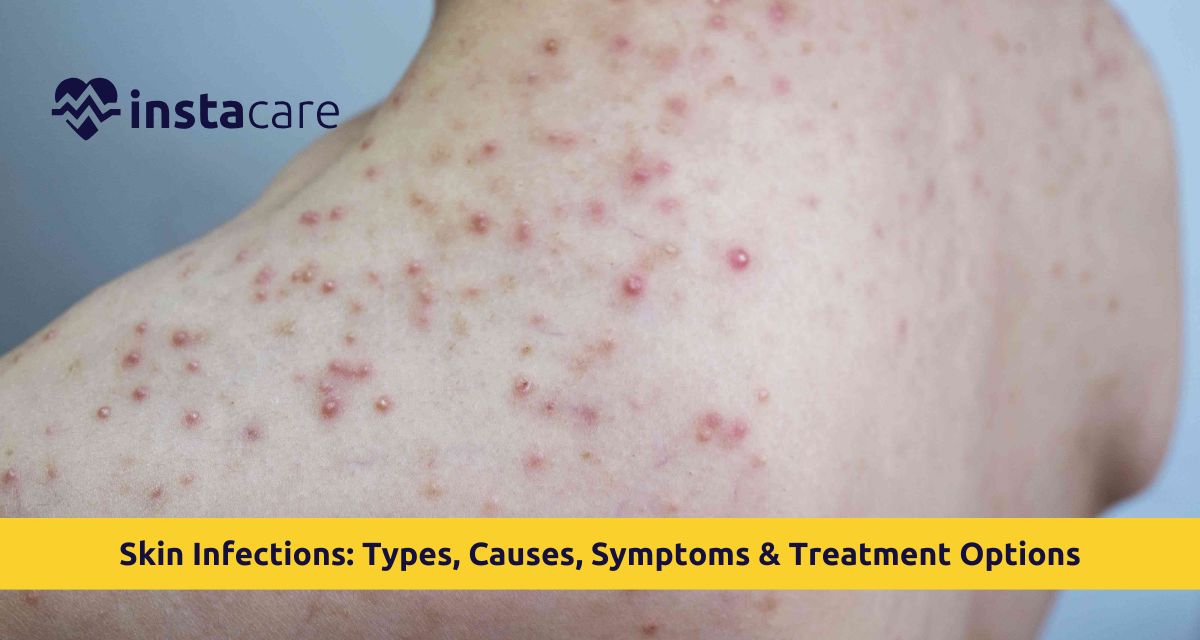
The microorganisms are harmful and penetrate the skin, causing inflammation, pain, and apparent changes. They may impact individuals of any age and vary in complexity, from mild and easily treatable to more severe infections. It is also important to understand the nature of skin infections, their causes and symptoms, and preventive measures to intervene and prevent infection. Most skin infections can be effectively managed with good hygiene, early treatment, and an understanding of the risk factors.
What Is a Skin Infection?
A skin infection is a condition that occurs when bacteria, fungi, viruses, or parasites enter the skin through a cut, hair follicles, or weakened areas of the skin. Good skin is a protective barrier; however, damage or low immunity may allow the pathogen to proliferate and spread. Skin infections can be confined to a single site or diffuse throughout the body. Others are infectious skin diseases, that is, they can be transferred between individuals through direct physical contact or contact with common objects.
What Causes Skin Infections?
Several internal and external factors that weaken skin health are known to cause skin infections. Common causes include:
- Bacteria through wound infections or cuts.
- Proliferation of fungi in warm humid places.
- Close contact exposure to the virus.
- Poor hygiene practices
- Weakened immune system
- Such chronic skin diseases as Eczema.
- Sweating or friction is excessive.
Knowledge of the causes of skin infections helps minimise risk and supports effective prevention.
Types of Skin Infections
Types of Skin Infections are categorised according to the causative organism.
Bacterial Skin Infection
Bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus cause bacterial skin infections. Common examples include:
- Cellulitis
- Impetigo
- Boils and abscesses
These infections are usually characterised by redness, heat, swelling and pain.
Fungal Skin Infection
Fungal skin infection occurs when the skin, hair or nail is covered by the growth of fungi. Typical fungal infections are:
- Athlete's foot
- Ringworm
- Candidiasis
They are normally found in the form of itchy, scaly or discolored patches and they grow well in wet conditions.
Viral Skin Infection
Viruses cause viral skin infections and are commonly transmitted through direct contact. Examples include:
- Warts
- Cold sores
- Chickenpox
These infections can be blistering, ruddy or as bumps.
Parasitic Skin Infections
The skin is also susceptible to parasitic infections, albeit infrequently. Examples include:
- Scabies
- Lice Infestations
Infections are typically characterised by itching and irritation.
Common Symptoms of Skin Infections
The symptoms of skin infection vary with the cause and extent. Typical signs include:
- Redness and inflammation
- Swelling or warmth
- Pain or tenderness
- Sensation of itching or burning.
- Posy lesions or blisters.
- Skin peeling or scaling
- Fever in severe cases
Timely management of symptoms is applied to avoid complications and transmission.
Risk Factors for Skin Infections
Some people are more likely to contract skin infections. Common risk factors include:
- Poor personal hygiene
- Cuts, wounds, or insect bites
- Diabetes or immune disease.
- Crowded living conditions
- Excessive sweating
Close contact in day-care or school results in skin infection in children. These risks are important to manage in order to have the long term skin.
Diagnosis of Skin Infections
Diagnosis typically begins with a physical examination by a physician. The physician can determine the appearance, position, and intensity of the infection. The additional tests can be:
- Skin swabs or cultures
- Major infections testing blood.
- Microscopic examination
Proper diagnosis facilitates an effective treatment method.
Treatment Options for Skin Infections
The treatment is dependent on the nature and severity of the infection. The usual methods of treatment are:
- Antibiotics against skin infection by bacteria.
- Antifungals Creams or oral antifungal agents used to treat fungus of the skin.
- Antiviral therapy of skin infection with viruses.
- Drug-treated lotions or shampoos.
- Adequate wound care and hygiene.
Early intervention prevents symptom aggravation and reduces the risk of transmission of contagious skin infections.
How to Prevent Skin Infections?
Prevention is an important measure for reducing skin infections. Good tips of preventing skin infection:
- Have a good personal hygiene.
- Wash hands regularly
- Keep skin clean and dry
- Ease cuts and wounds immediately.
- Do not use personal things.
- Wear breathable clothing
- Enhance immunity through a balanced diet.
The practices are of particular importance to skin infection among children.
When to See a Doctor?
Medical care is required when:
- The symptoms become severe and contagious.
- Changes in skin are accompanied by fever.
- Pus or severe pain is present
- Home care does not enhance infection.
- The patient is either diabetes or has a weakened immune system.
Consultation at the initial stage will avoid severe complications.
Conclusion
Skin infections are familiar and treatable diseases that have to be treated promptly. Knowledge about the possible nature of skin infections, the ability to identify their early manifestations, and adherence to the related treatment modalities can help to avoid complications and achieve a quicker recovery process. Healthy skin is a goal that can be obtained with appropriate cleanliness, preventive actions, and expert treatment in case of necessity among people of any age.
Please book an appointment with the Best Dermatologist in Lahore, Karachi, Islamabad, and other major cities of Pakistan through InstaCare, or call our helpline at 03171777509 to find a verified doctor for your condition.